📝 Note: This article was last updated on Jan. 21, 2026. We regularly update the information to ensure you have the latest insights! 😊
At the start
When software agencies take on new client projects, the pressure is almost always the same: clients want results fast, but they also expect stability, flexibility, and long-term maintainability.
That is why many agencies turn to no-code and low-code tools to quickly build prototypes or PoCs.
However, not every no-code or low-code platform is suitable for long-term client delivery. As requirements evolve, workflows become more complex, and access control needs to be more granular, the limitations of many tools start to surface.
Within developer communities, opinions on no-code vary widely. Some see it as a powerful way to ship faster, while others worry about vendor lock-in, architectural constraints, and the cost of maintaining complex systems over time.
From the perspective of teams delivering real client systems, this raises a key question: among open-source no-code and low-code platforms, which ones are truly suitable for building systems that clients will rely on for years, not just weeks?
💡Read more: 6 Open-Source No/Low-Code Tools for Building PoCs
💬Hey, you’re reading the NocoBase blog. NocoBase is the most extensible AI-powered no-code/low-code development platform for building enterprise applications, internal tools, and all kinds of systems. It’s fully self-hosted, plugin-based, and developer-friendly. → Explore NocoBase on GitHub
Client Projects vs. Internal Projects
Many no-code platforms are built around a simple assumption: they are primarily used for internal projects and maintained by the same team over a long period of time.
Once you move into client-facing projects, this assumption quickly breaks down.
When a system is built for external clients, the delivery model, technical requirements, and long-term responsibilities change in fundamental ways.
First, changing requirements are the norm
In client projects, the first release is rarely the finish line. Requirements evolve constantly. Clients add new features, adjust workflows, and sometimes even reverse earlier decisions. This means a no-code platform must support continuous iteration without breaking existing functionality or forcing costly rework.
Second, deployment and delivery are far more complex
Many client projects are eventually deployed into the client’s own environment, such as on-premise servers, private clouds, or restricted internal networks. A suitable platform must support self-hosting and make deployment, upgrades, and migrations predictable and controllable, rather than hidden risks that surface months later.
Third, delivery is only the beginning
For teams building client systems, going live does not mean the project is finished. Ongoing changes, bug fixes, and feature extensions continue long after launch. If a platform is not designed for long-term maintenance, each new request increases technical debt and operational friction.
Finally, cost control determines whether a project is actually profitable
This is the most practical and often overlooked factor. If a platform is expensive to modify, extend, or maintain over time, a project can keep losing money even after a successful launch. Choosing the right platform is ultimately about controlling long-term labor costs and reducing unpredictable delivery risks, not just shipping faster at the beginning.
Key Comparison Dimensions for Client Project Delivery
| Dimension | NocoBase | Appsmith | Budibase | NocoDB | ToolJet | Directus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open source | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Self-hosted deployment | ✅ Built-in, production-ready | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Data modeling capability | Strong (relational, model-first) | Medium | Medium | Weak (table-centric) | Medium | Strong |
| Relational data support | Full support (many-to-many, junction tables, constraints) | Limited | Limited | ⚠️ Not a core focus | Limited | Strong |
| Permission system (RBAC) | System-level, fine-grained (role, data, action) | Basic | Basic | Basic | Basic | Strong |
| Business processes & workflows | Built-in, designed for real business processes | Weak | Medium | ❌ | Medium | ❌ |
| Extension & customization approach | Plugin-based architecture; frontend JS blocks for lightweight extensions | Primarily custom JS | Limited | ❌ | Primarily custom JS | Hooks-based |
| Support for evolving requirements | Strong, designed for continuous iteration | Average | Average | Weak | Average | Medium |
| Reuse across multiple client projects | Well suited (templates, plugins, repeatable patterns) | Average | Average | Not suitable | Average | Average |
| Suitability for long-term client delivery | High | ⚠️ Limited | ⚠️ Limited | ❌ | ⚠️ Limited | ⚠️ Limited |
NocoBase
Website:https://www.nocobase.com
GitHub:https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase
GitHub stars: 20.8k
NocoBase is an open-source, self-hosted AI no-code and low-code platform built around data models and a plugin-based architecture. It is designed for building scalable, production-ready business systems rather than lightweight internal tools.
From a client project delivery perspective, NocoBase behaves less like a fixed-feature no-code tool and more like a flexible, extensible development foundation. This makes it particularly suitable for agencies and service teams responsible for long-term delivery, maintenance, and ongoing system evolution.
When does NocoBase make sense for client projects?
In real-world client delivery scenarios, NocoBase is especially well suited for the following types of projects.
1.Projects with clear or evolving AI requirements
NocoBase integrates AI directly into the system through AI Employees. Instead of treating AI as an external add-on, AI is modeled as a first-class system role that can participate in forms, workflows, and data operations, all within clearly defined permission boundaries.
This approach works well for projects that:
- Need intelligent assistance inside business workflows
- Want to introduce AI gradually, without redesigning the system later
- Require strict control over what AI can access and modify
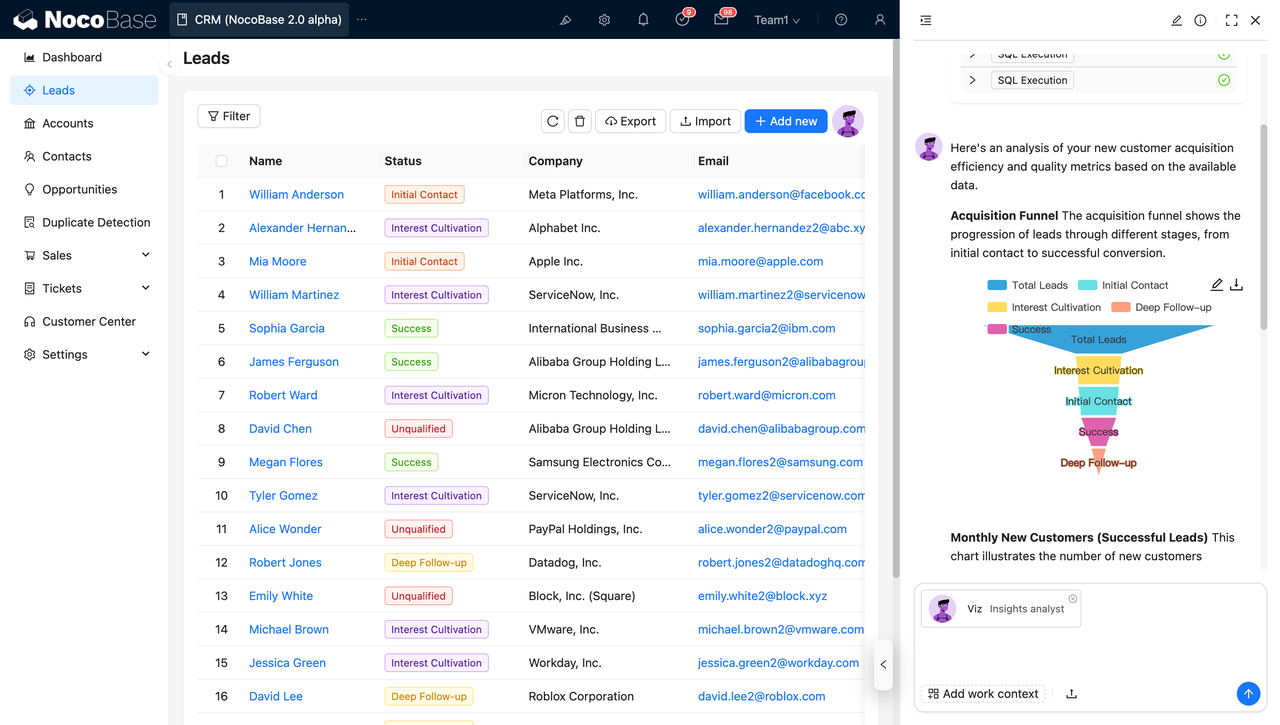
For example, an AI Employee can read and analyze lead data stored in the system and assist sales teams with classification, enrichment, or follow-up suggestions.
2.Projects where data relationships, permissions, and workflows define the core complexity
Many client systems are not complex because of UI, but because of:
- Multiple business entities with relationships
- Role-based and data-level permissions
- Cross-role approval flows and business processes
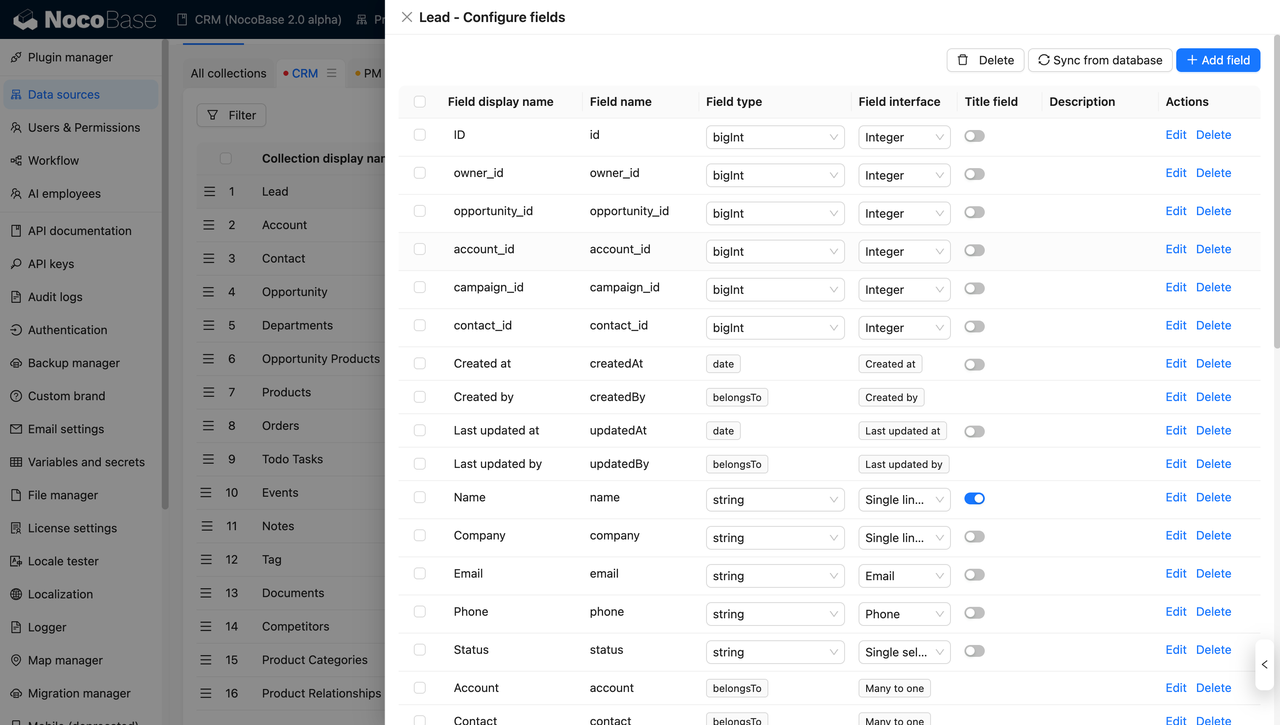
NocoBase provides system-level support for relational data modeling, RBAC, and workflows, which significantly reduces long-term maintenance costs compared to tools that rely heavily on custom scripts.
At its core, NocoBase is data-driven. It supports:
- A primary internal database
- External databases such as MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, and Oracle
- API-based data sources
UI blocks and user actions are fully decoupled from underlying data sources, resulting in an architecture closer to traditional software development and far better suited for complex business scenarios.
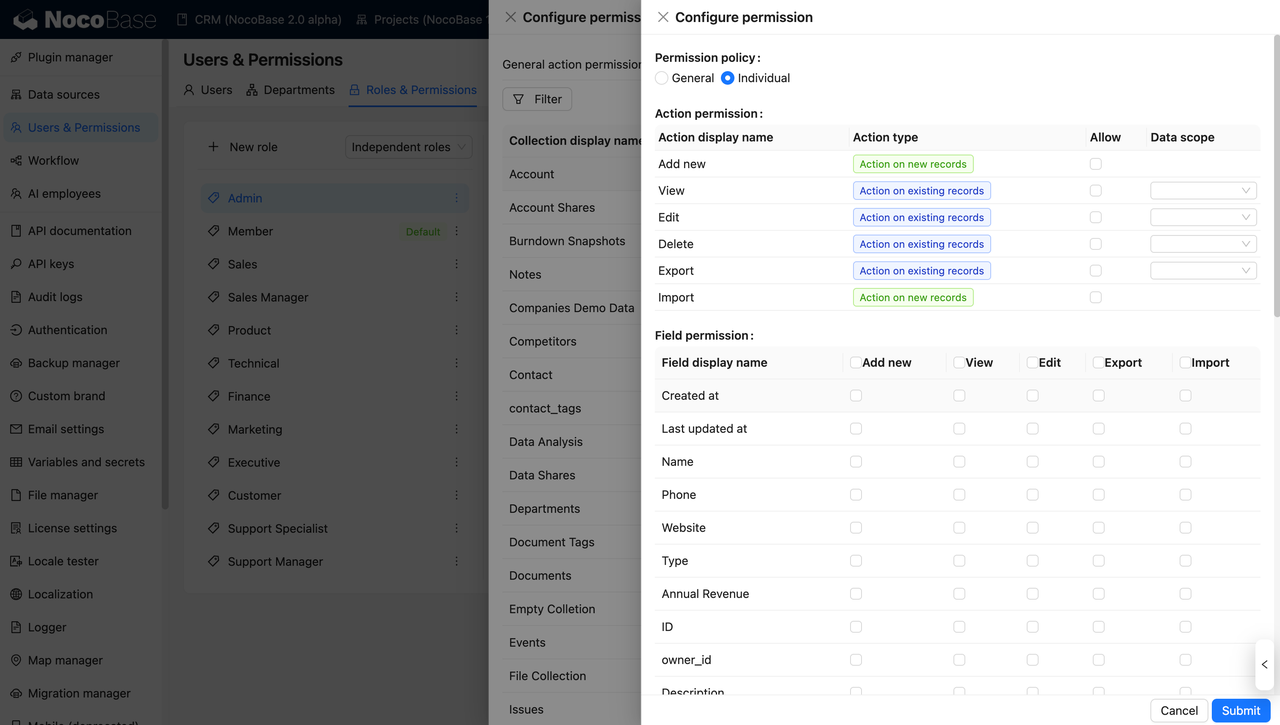
NocoBase also supports field-level permission control, which is critical for multi-role client systems.
3.Systems with continuously evolving requirements
In client projects, change is the default. New fields, new relationships, and new workflows are introduced long after the first release.
NocoBase follows a model-first approach: stabilize the data structure first, then layer UI, workflows, and permissions on top. This makes it easier to extend systems over time without breaking existing functionality or accumulating fragile workarounds.
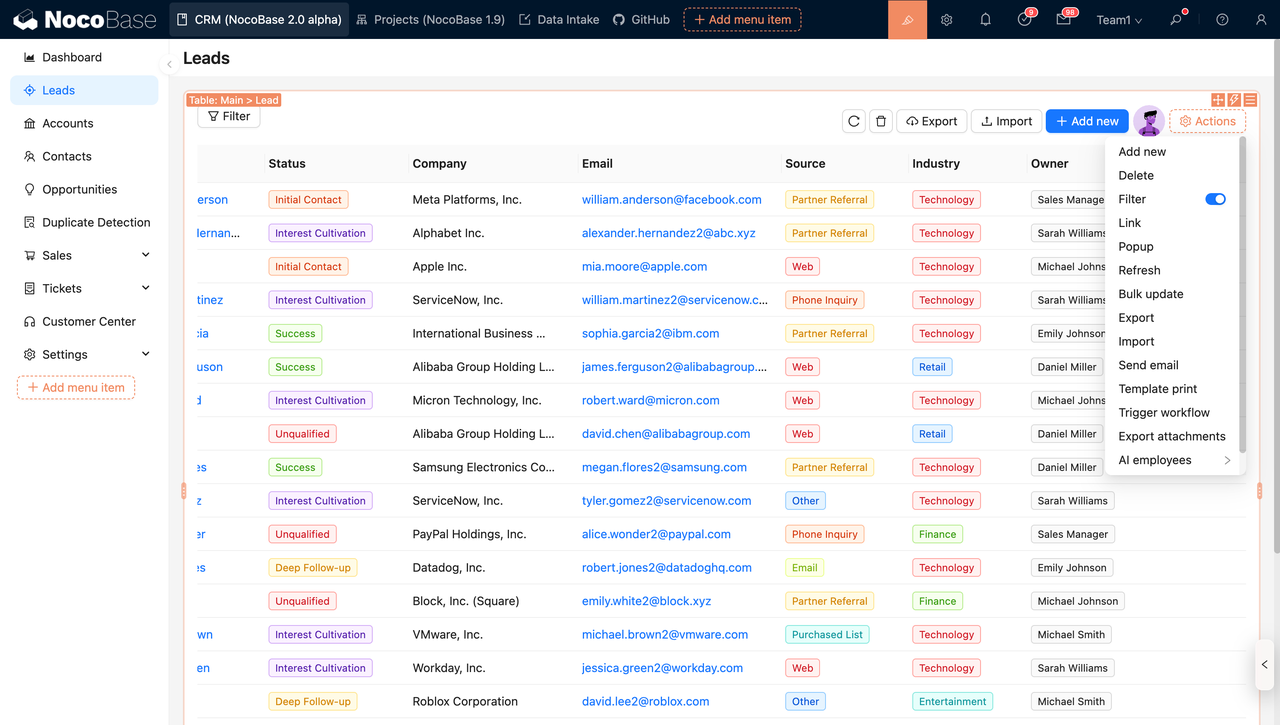
Adjusting the UI is straightforward. Teams can enter edit mode directly from the interface and iterate quickly without touching the underlying data model.
4.Projects that require customization and extension
When built-in features are not enough, NocoBase allows code-level extensions through its plugin mechanism, rather than forcing teams into predefined capabilities.
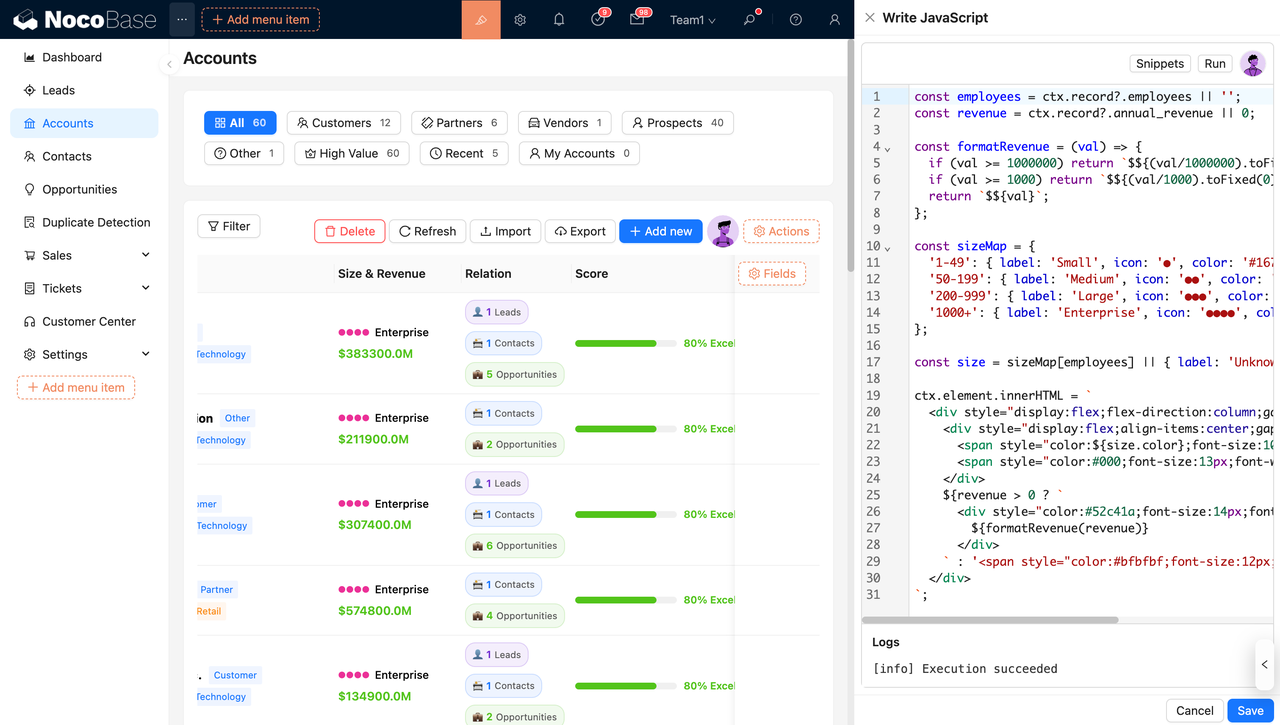
For lighter customization needs, frontend JS blocks can be used to implement custom field rendering, interactions, or integrations. This combination allows teams to balance speed and flexibility without sacrificing maintainability.
Typical client systems built with NocoBase
In practice, NocoBase is commonly used to deliver:
- CRM systems
- Project and delivery management systems
- Lightweight ERP and business management systems
- Customer success and after-sales systems
- Approval and workflow systems
- Industry-specific customized management systems
What these systems have in common is not their domain, but their structure: clear data models with complex relationships, continuously evolving requirements, and a strong need for long-term maintenance and controlled delivery costs.
Appsmith
Website:https://www.appsmith.com/
GitHub:https://github.com/appsmithorg/appsmith
GitHub stars: 38.7k
Appsmith is an open-source, self-hosted no-code and low-code platform designed for rapidly building API-driven internal tools and admin interfaces. Its core strength lies in UI composition, direct API bindings, and fast interaction with existing services.
From a client project delivery perspective, Appsmith is best suited for UI-centric, tool-focused applications, rather than full-fledged business systems with complex data models and workflows.
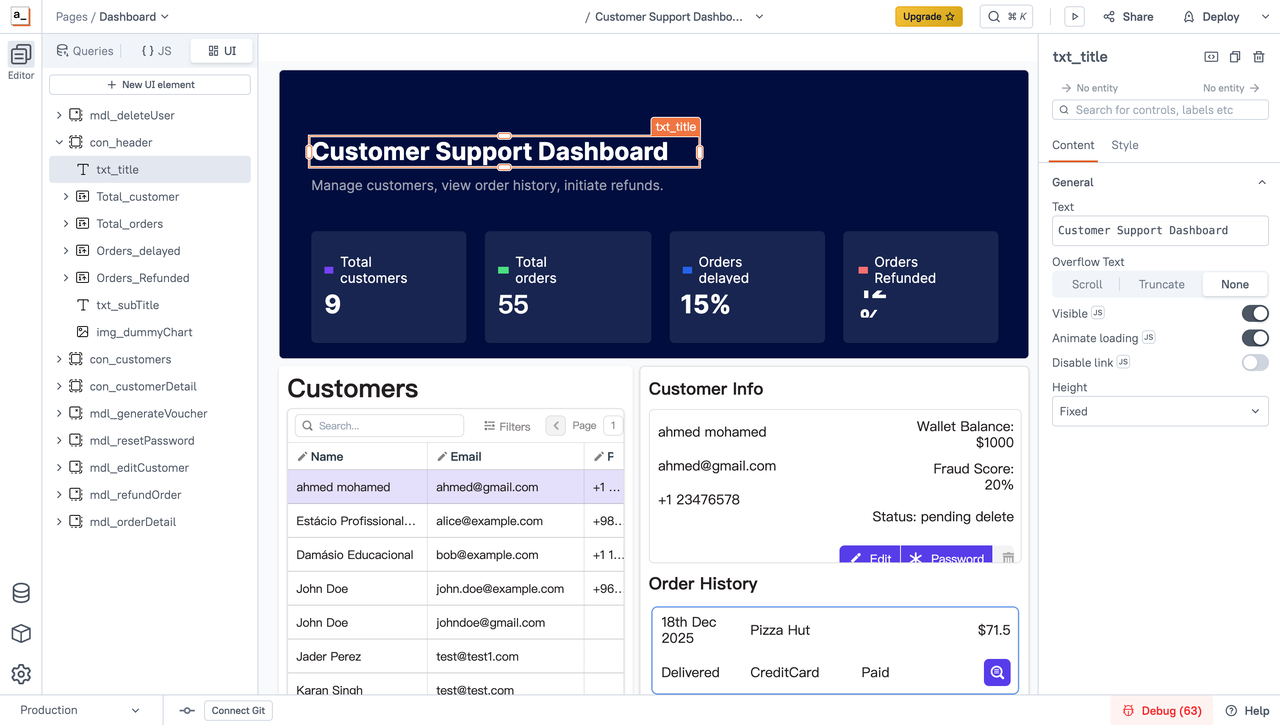
When does Appsmith make sense for client projects?
In real-world client delivery scenarios, Appsmith is typically a good fit for the following types of projects.
1.UI- and operation-focused tools
When the primary goal is to quickly build admin dashboards, operational panels, or data manipulation interfaces, Appsmith’s component-based UI and direct API bindings can significantly accelerate delivery.
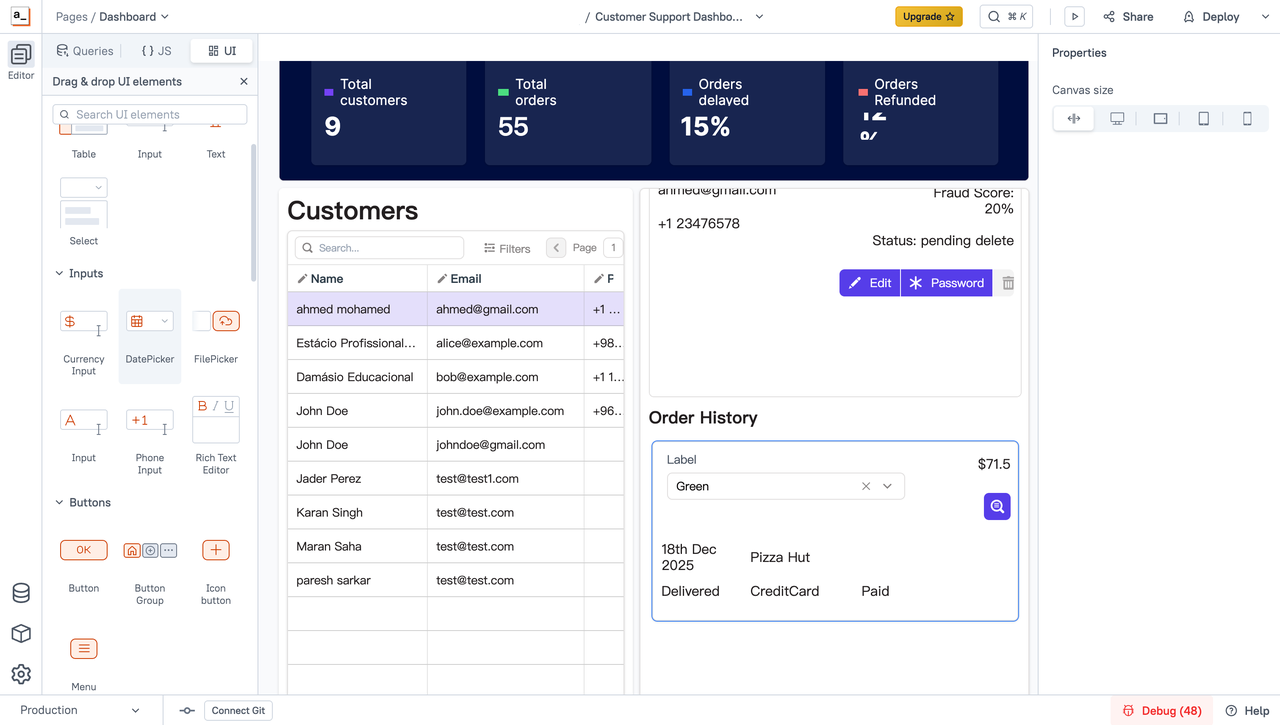
2.Projects with an existing backend
If the client already has stable backend services or databases and only needs a frontend layer for querying, editing, and triggering basic actions, Appsmith is easy to adopt and quick to roll out.
In these cases, Appsmith acts as a thin UI layer on top of existing systems, avoiding the need for heavy data modeling or workflow configuration.
3.Projects with relatively stable requirements
When data fields, relationships, and workflows are largely fixed and unlikely to change frequently, Appsmith can be delivered efficiently without extensive upfront modeling or architectural planning.
This makes it suitable for tools where the structure is known early and long-term evolution is limited.
Typical client tools built with Appsmith
In practice, Appsmith is commonly used to deliver:
- Internal admin dashboards
- Data querying and maintenance tools
- Operational or customer support interfaces
- API-driven business tools
- Simple internal form-based systems
What these tools have in common is a clear focus on UI efficiency and operational convenience, with limited complexity in data relationships, workflows, and permission models.
Budibase
Website:https://budibase.com/
GitHub:https://github.com/Budibase/budibase
GitHub stars: 27.5k
Budibase is an open-source, self-hosted no-code platform designed for rapidly building business applications on top of databases or table-based data. It emphasizes ease of use, prebuilt components, and a template-first development experience.
From a client project delivery perspective, Budibase occupies a similar position to Appsmith. It is particularly strong at building UI-driven tools and straightforward business applications.
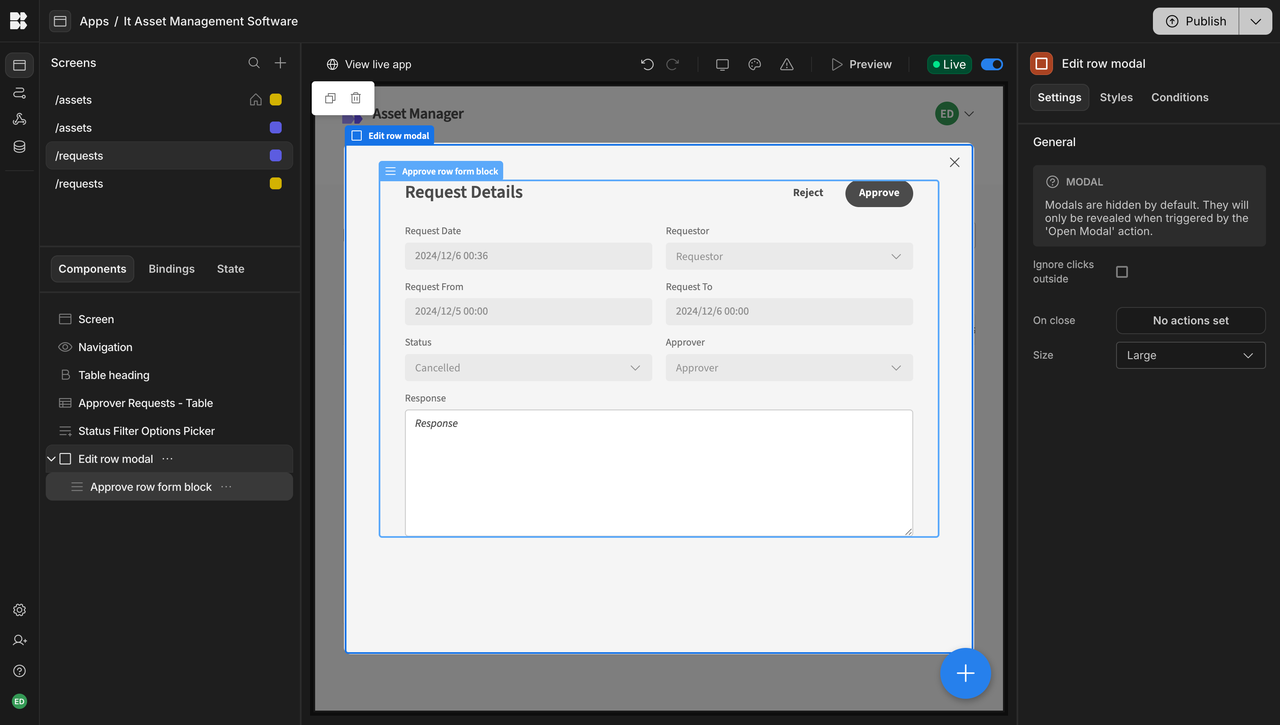
When does Budibase make sense for client projects?
In real-world client delivery scenarios, Budibase is typically a good fit for the following types of projects.
1.Low- to medium-complexity data management systems
When a project primarily involves data entry, querying, basic updates, and status tracking, and the underlying data relationships are relatively simple, Budibase can be delivered efficiently with minimal setup.
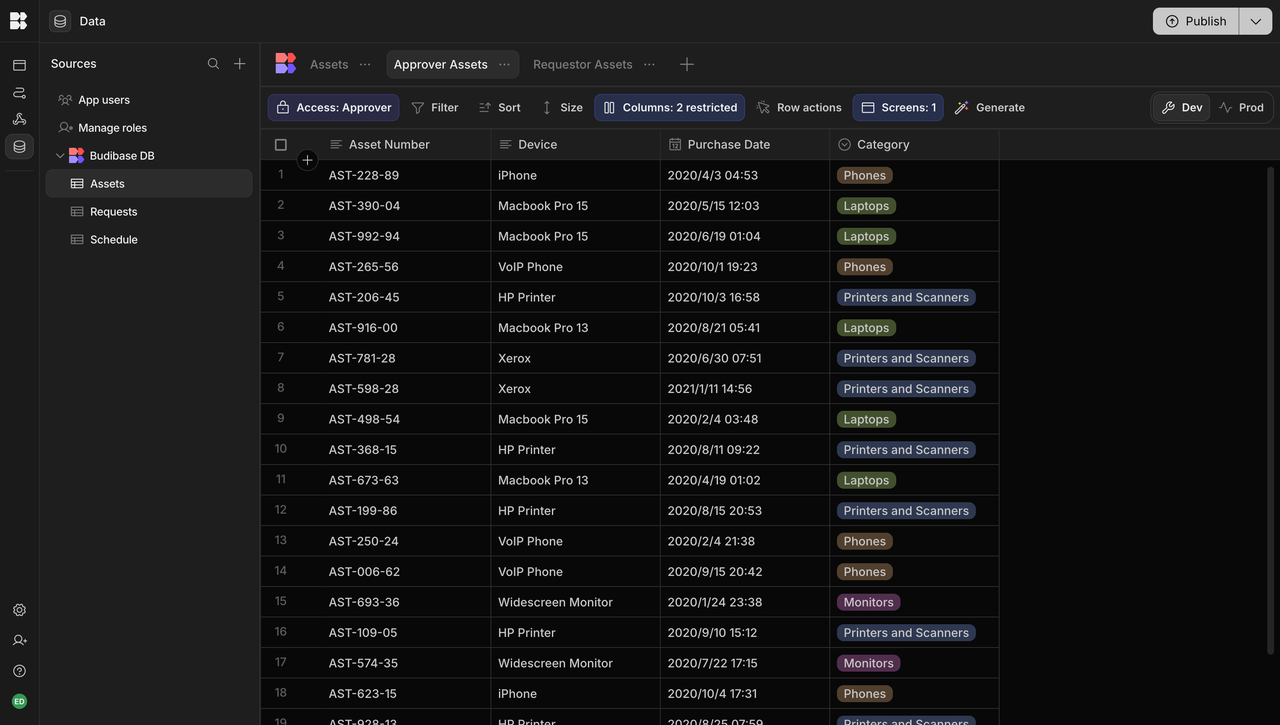
2.Projects with tight delivery timelines
Budibase’s configuration model and ready-to-use UI components make it well suited for projects where time-to-first-version is the main constraint.
3.Applications built on existing databases or table schemas
If a client already has a well-defined database or table schema, Budibase can be layered directly on top of it to build application interfaces.
Typical client systems built with Budibase
In practice, Budibase is commonly used to deliver:
- Simple CRM or customer information management systems
- Internal data entry and management tools
- Lightweight approval or status-tracking applications
- Operational tools used by business or operations teams
What these systems have in common is a focus on straightforward data operations and UI efficiency, with relatively flat data models, limited workflow and permission complexity, and modest requirements for long-term extensibility.
NocoDB
Website:https://nocodb.com/
GitHub:https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb
GitHub stars: 59.2k
NocoDB is an open-source, self-hosted no-code platform designed to turn relational databases into Airtable-style visual tables, with a strong emphasis on data access, collaboration, and spreadsheet-like interaction.
From a client project delivery perspective, NocoDB functions primarily as a database visualization and collaboration layer. It excels at making structured data more accessible, but intentionally keeps business logic and process complexity to a minimum.
When does NocoDB make sense for client projects?
In real-world client delivery scenarios, NocoDB is best suited for a relatively narrow, table-centric set of use cases.
1.Spreadsheet-driven data management
When a client’s core requirement is still collaborative, spreadsheet-style data work, but with better access control and deployment flexibility than Excel or Google Sheets, NocoDB can be delivered quickly with minimal overhead.
2.Clients explicitly seeking an open-source Airtable alternative
For teams that want to avoid SaaS products and prefer a self-hosted, open-source alternative to Airtable, NocoDB is a direct and intuitive choice.
3.Projects with stable and simple data structures
If table schemas are largely fixed and there is little need for complex relationships or evolving business logic, NocoDB is a practical option.
It supports external databases such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, making it suitable for exposing existing data in a more user-friendly format without restructuring the underlying schema.
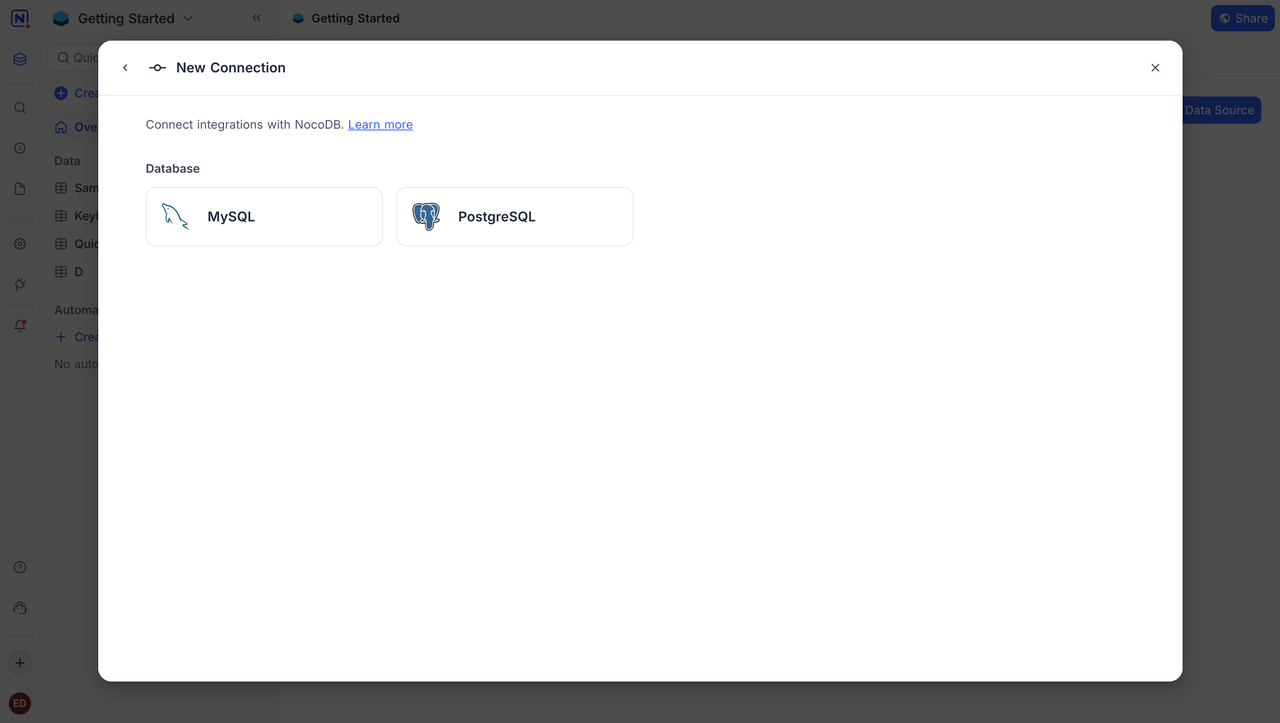
Typical client systems built with NocoDB
In practice, NocoDB is commonly used to deliver:
- Excel or Airtable replacements
- Simple customer, inventory, or asset records
- Data entry and sharing tables
- Spreadsheet-centric internal collaboration tools
What these systems have in common is a strong focus on table-based operations, with lightweight business logic and limited requirements for workflows, permissions, and long-term extensibility.
ToolJet
Website:https://www.tooljet.com/
GitHub:https://github.com/ToolJet/ToolJet
GitHub stars: 37.1k
ToolJet is an open-source, self-hosted low-code platform that combines AI-assisted app generation, a visual builder, and integrations with databases and APIs. It allows teams to bootstrap applications using natural language prompts and then refine them through visual configuration.
From a client project delivery perspective, ToolJet blends visual low-code development with fast, prompt-based scaffolding. Its strengths lie in rapid prototyping and internal business tools, rather than serving as a foundation for complex, long-lived business systems.
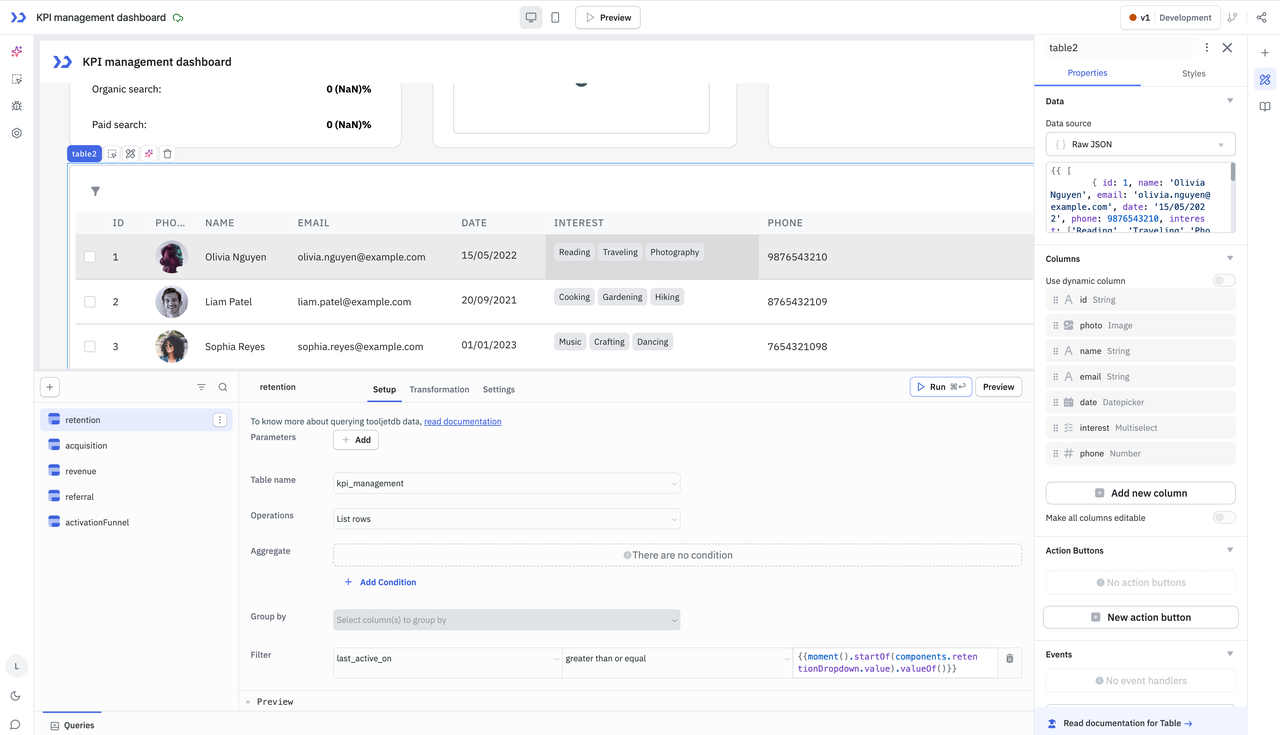
When does ToolJet make sense for client projects?
In real-world client delivery scenarios, ToolJet is most effective in the following situations.
1.Projects that require rapid prototyping from requirements
ToolJet allows teams to describe requirements in natural language and generate an initial application structure. This makes it well suited for quickly producing prototypes, demos, or early-stage versions of client applications.
ToolJet can significantly shorten the path from idea to working interface.

2.Data-integration-driven internal tools
When the primary goal is to consolidate data from databases, APIs, or existing business systems into dashboards, admin panels, or operational interfaces, ToolJet’s visual builder and data connectors help reduce development effort.
3.Business logic with simple workflows or automation
ToolJet supports event triggers, basic workflow steps, and lightweight automation logic. This is sufficient for straightforward business process automation, such as form submissions, status updates, or simple approval actions.
Typical client tools built with ToolJet
In practice, ToolJet is commonly used to deliver:
- Internal management or operations tools
- Data querying and editing backends
- Simple business operation interfaces
- API-driven management panels
What these tools have in common is a strong focus on UI efficiency and fast iteration, with limited reliance on system-level data modeling, complex workflows, or advanced permission control.
Directus
Website:https://directus.io/
GitHub:https://github.com/directus/directus
GitHub stars: 33.7k
Directus is an open-source, self-hosted headless data platform that sits on top of existing databases to provide unified data access, fine-grained permission control, and auto-generated APIs. It is commonly used as a Headless CMS or a centralized data service layer.
From a client project delivery perspective, Directus is best understood as a data and content management layer, rather than a full application framework responsible for UI, workflows, or end-to-end business processes.
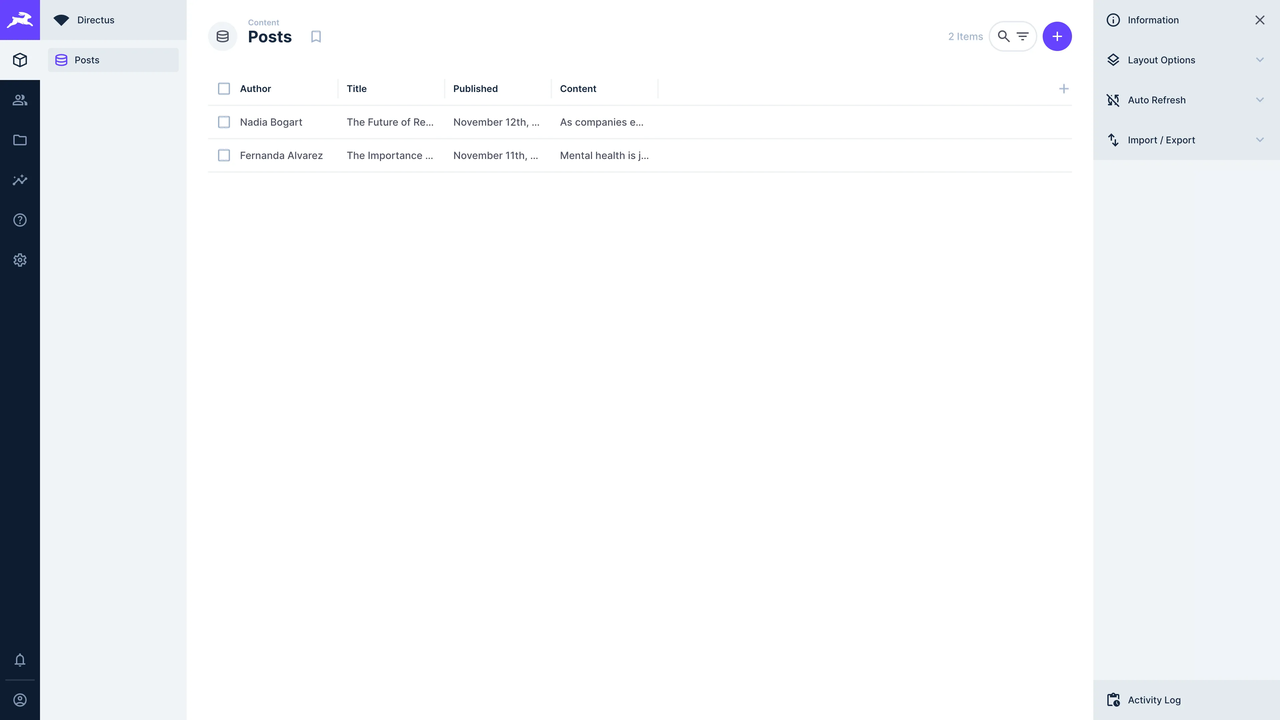
When does Directus make sense for client projects?
In real-world client delivery scenarios, Directus is a strong fit for projects where data structure, access control, and API consistency are the primary concerns.
1.Content- or data-centric projects
When the core focus of a project is managing content structures, defining data schemas, and exposing clean APIs to multiple consumers, Directus is a natural choice.
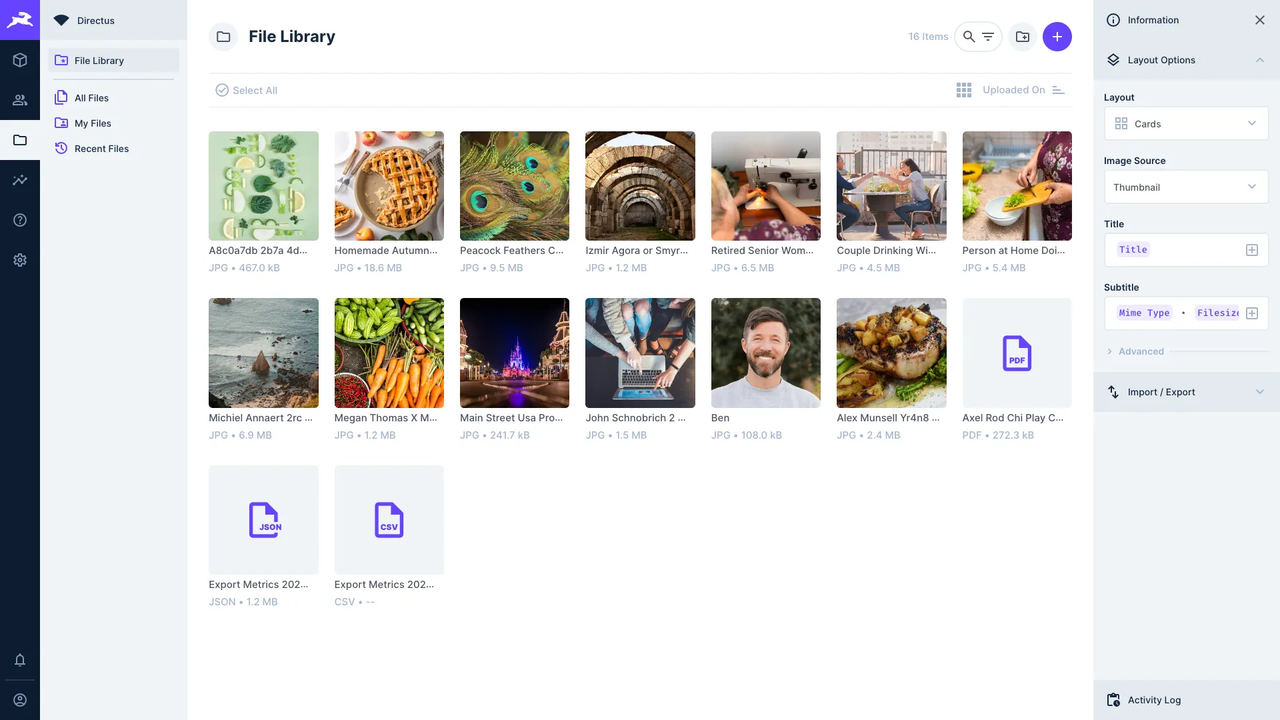
2.Projects requiring stable data models and strict access control
Directus offers robust, data-level permission management and automatic API generation, making it well suited for environments with strict governance, compliance, or data access requirements.
3.Acting as a data backbone or backend service
In many client projects, Directus is most effective when positioned as a foundational data service, rather than the application layer itself.
Typical client systems built with Directus
In practice, Directus is commonly used to deliver:
- Headless CMS and content management systems
- Data management and distribution platforms
- Backend service layers for frontend applications
- Shared data platforms used across multiple applications
What these systems have in common is a strong emphasis on data structure, access control, and API reliability, with relatively limited focus on business workflows, UI interactions, or application-layer process orchestration.
Summary
Each open-source no-code platform excels in different client delivery scenarios. The key is not which tool is “better,” but which layer of the system you are actually building.
- Appsmith, ToolJet, and Budibase
These tools focus primarily on the application and tooling layer. They are well suited for rapidly building internal tools, admin panels, and operational interfaces, offering fast delivery at the cost of limited system depth and long-term extensibility.
- NocoDB
NocoDB functions essentially as a spreadsheet collaboration and database visualization tool. It is a strong replacement for Excel or Airtable when teams want better control and self-hosting, but it is not designed for complex business systems.
- Directus
Directus operates as data and content infrastructure. It is commonly used as a backend service or a centralized data layer, especially when data governance and API consistency are the primary concerns.
- NocoBase
NocoBase is closer to an extensible business system foundation. It is particularly well suited for client projects with continuously evolving requirements, complex data relationships, and permissions and workflows at the core of the system.
In the end, the best tool is the one that fits the delivery scenario, system boundaries, and long-term responsibility of your project.
❤️ Thanks for reading to the end. If you found this article useful, feel free to share it with others who build and deliver real client systems.
Related reading:
- How to Quickly Build a Real System to Replace Excel: A Complete Guide
- Top 5 Open-Source AI Internal Tools on GitHub
- The 8 Best Google Sheets Alternatives (Specs & Pricing)
- 6 Open-Source No/Low-Code Tools for Building PoCs
- A Developer’s Technical Decision Guide to No-Code and Low-Code (2026)
- 6 In-Depth Comparison of RBAC in Enterprise-Grade No-Code/Low-Code Platforms
- 14 AI-Powered Low-Code Platforms on GitHub Worth Watching
- Top 11 Open Source No-Code AI Tools with the Most GitHub Stars
-nwyljo.PNG)