📝 Note: This article was last updated on Jan. 21, 2026. We regularly update the information to ensure you have the latest insights! 😊
✨ Check out our updated 2026 roundup of open-source AI projects on GitHub: https://www.nocobase.com/en/blog/best-open-source-ai-projects-github-2026
About a month ago, I came across a highly discussed post on Hacker News — “Stop Building AI Agents”
In the post, the author shared a personal experience: he built a “research crew” with CrewAI: three agents, five tools, perfect coordination on paper. But in practice, the researcher ignored the web scraper, the summarizer forgot to use the citation tool and the coordinator gave up entirely when processing longer documents. It was a beautiful plan falling apart in spectacular ways.
The flowchart below was created by the author after countless rounds of debugging and failed attempts, summarizing his decision guide for Should I use an Agent.
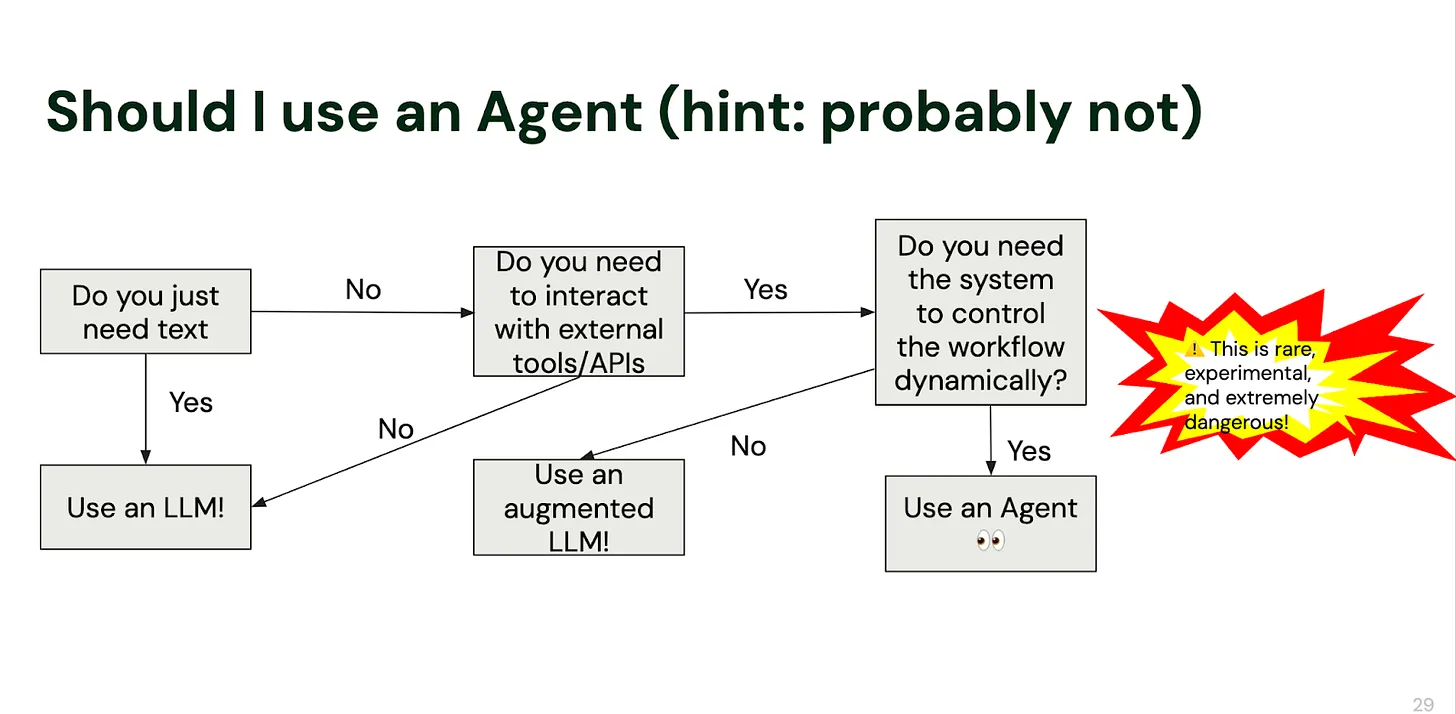
Image source: https://decodingml.substack.com/p/stop-building-ai-agents
The article distilled an important principle: agents work best in unstable processes where humans remain in the loop for oversight — in these scenarios, an agent’s exploratory and creative capabilities often outperform a rigid workflow.
- Recommended scenarios: data science assistant (auto-generating SQL, creating visualizations, exploring data trends); creative writing partner (brainstorming ideas, refining copy); code refactoring assistant (suggesting optimizations, detecting potential issues). In these cases, humans can continuously evaluate results and correct deviations.
- Not recommended for: mission-critical enterprise automation (key business processes that cannot risk instability from LLM-driven decisions); high-stakes decision-making (finance, medical diagnosis, legal compliance — areas that require deterministic logic).
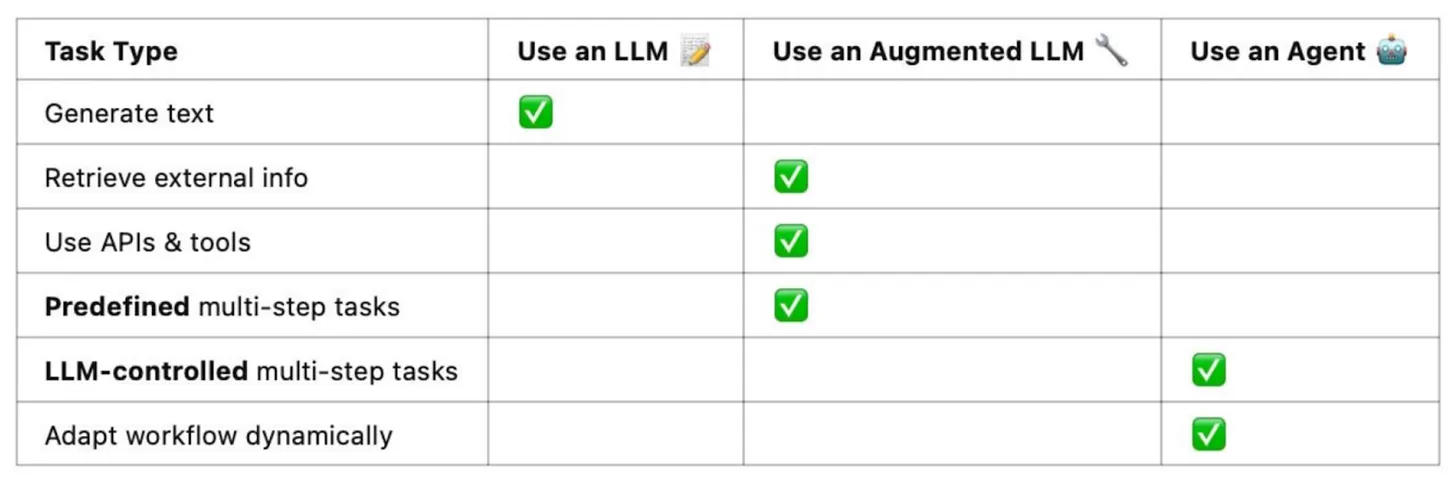
Image source: https://decodingml.substack.com/p/stop-building-ai-agents
If you’ve read the above and still feel your business scenario is a good fit for building an agent, this article will walk you through the top 18 open source agent projects on GitHub by star count. For each, we’ll analyze their strengths and limitations from three perspectives — project overview, core features, and use cases — helping you maximize the value of agents in the right contexts.
💬 Hey, you’re reading the NocoBase blog. NocoBase is the most extensible AI-powered no-code/low-code development platform for building enterprise applications, internal tools, and all kinds of systems. It’s fully self-hosted, plugin-based, and developer-friendly. → Explore NocoBase on GitHub
💡 You might also enjoy our previous popular GitHub project roundups (some projects appear in multiple themes):
- Top 20 Open Source AI Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 8 Open Source MCP Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 40 Open-source Developer Tools with the Most GitHub Stars
No.1: Dify
- GitHub Star: 110k
- GitHub: https://github.com/langgenius/dify
- Website: https://dify.ai/
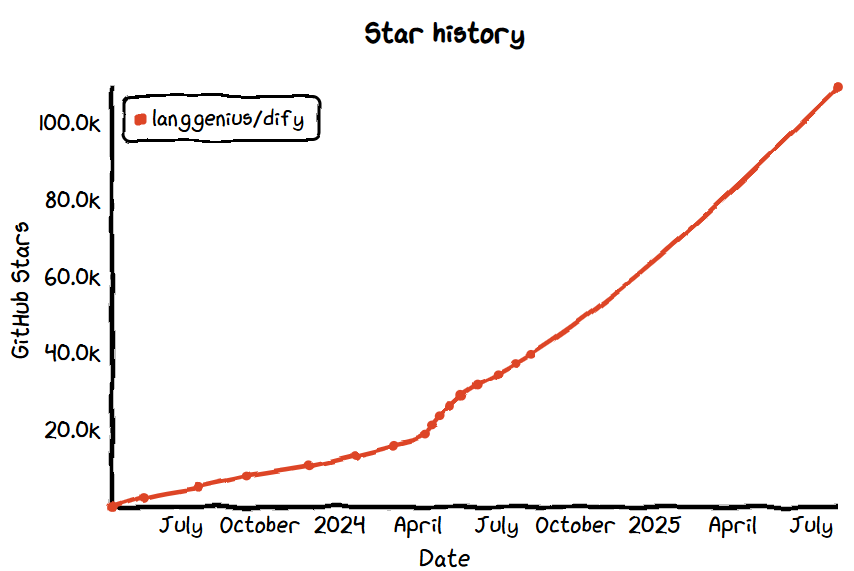
Overview:
Dify is an open-source LLM application development platform that combines an intuitive visual interface, RAG workflows, agent capabilities, model management, and full-stack observability. It enables developers to rapidly build, debug, and deploy AI applications.
Core Features:
- Visual Workflow Orchestration: Drag-and-drop builder that allows developers to design and test complex AI workflows directly on a canvas, including prompts, model calls, and task chaining.
- RAG Pipeline Support: Ingests multi-format documents (e.g., PDF, PPT), automatically extracts content, and builds retrieval pipelines for knowledge-augmented generation.
- Comprehensive Model Ecosystem & Prompt Editor: Compatible with GPT, Mistral, Llama3, and all OpenAI API-compatible models. Offers unified model management and prompt tuning, simplifying model switching and performance comparison.
Use Cases:
- Building intelligent customer service and QA systems
- Integrating with enterprise knowledge bases
- Rapid deployment of content generation tools
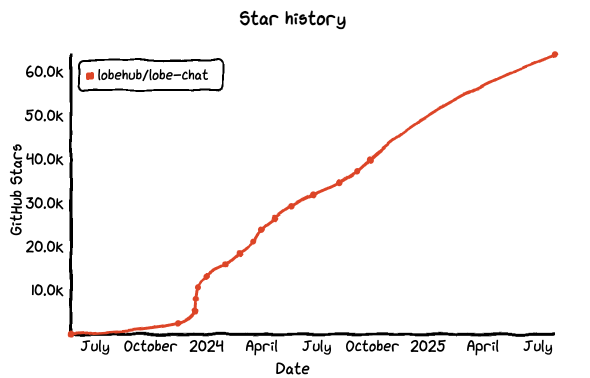
No.2: Lobe Chat
- GitHub Star: 64.3k
- GitHub: https://github.com/lobehub/lobe-chat
- Website: https://lobechat.com/
Overview:
Lobe Chat is an open-source multi-model chat and application platform with a strong focus on UX. It supports voice, visual recognition, multimodal input, a plugin marketplace, mobile optimization, and multi-user management.
Core Features:
- Multimodal & Plugin Support: Handles voice conversations, image recognition and generation, and can extend functionality via a plugin marketplace to support diverse interaction needs.
- Agent Index Platform: Community-driven index where users can browse, add, or submit custom assistants for easier extension and reuse.
- Unified Model Integration: Provides a unified API interface and modular architecture to easily connect with model providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, and Ollama, making platform migration and upgrades seamless.
Use Cases:
- Quickly building high-interaction, multimodal AI chat applications
- Deploying domain-specific assistants
No.3: RAGFlow
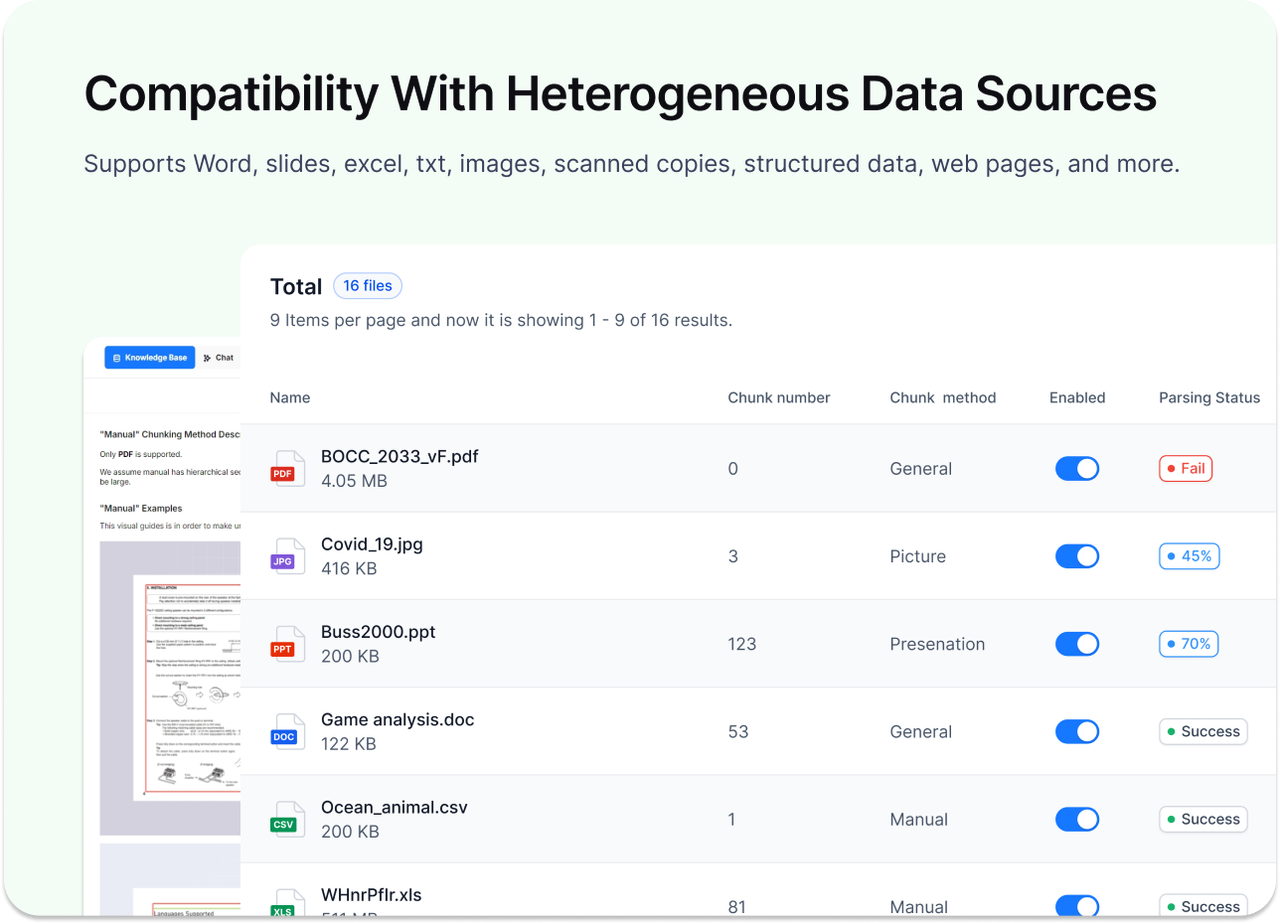
- GitHub Star: 62.1k
- GitHub: https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow
- Website: https://ragflow.io/

Overview:
RAGFlow is an open-source RAG engine focused on deep document understanding, designed to provide high-quality, explainable Q&A and agent services for enterprises and individuals. It can process complex document formats and deliver citation-based answers with visual block management.
Core Features:
- Deep Document Understanding: Excels at parsing unstructured content such as PDF, Word, PPT, Excel, and images, extracting searchable information blocks to ensure generated content is factual and verifiable.
- RAG Q&A with Citation Tracking: Combines vector retrieval with LLMs to generate cited answers, while allowing manual adjustments to retrieval blocks for improved accuracy.
- Flexible Deployment & Integration: Offers Docker Compose deployment and integration with various LLMs.
Use Cases:
- Building document-driven Q&A systems and knowledge assistants
- Implementing content auditing and citation tracking
- Deploying RAG applications that handle complex file structures
No.4: OpenHands
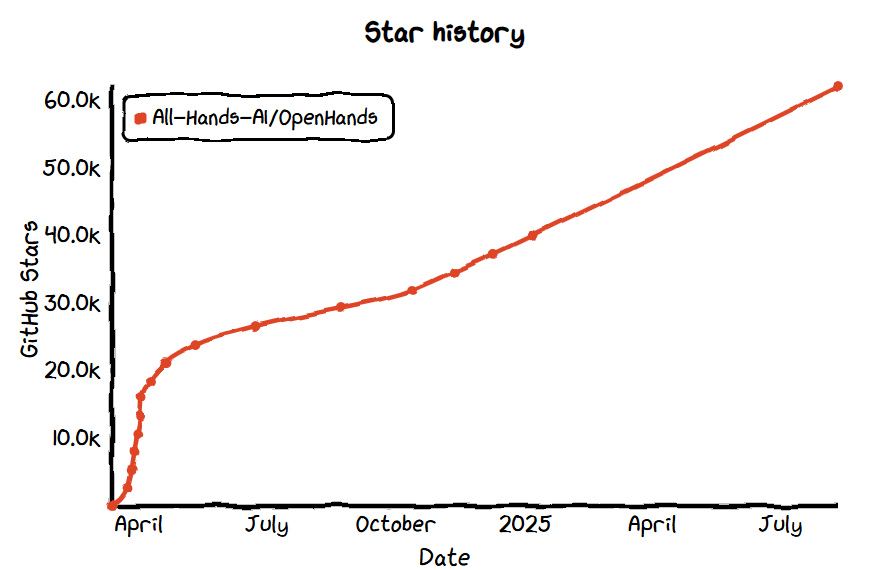
- GitHub Star: 62k
- GitHub: https://github.com/All-Hands-AI/OpenHands
- Website: https://all-hands.dev/
Overview:
OpenHands is built around the idea that AI should “write less code, get more done” — offering capabilities such as code editing, command execution, web browsing, and API calls.
As an MIT-licensed open-source project, OpenHands can be deployed locally via Docker or accessed through OpenHands Cloud SaaS, which includes initial usage credits for quick trials. With continuous updates, OpenHands has evolved into a comprehensive developer-focused AI platform, now featuring a universal agent controller, multi-agent collaboration, multi-session management, and secure sandbox execution.
Core Features:
- General Developer Agent Capabilities: Agents can perform tasks like modifying code, running commands, browsing the web, and calling APIs, mimicking the workflows of human developers.
- Multi-Agent Collaboration & Session Management: Supports multiple agents working together, with built-in session management components (Session, EventStream, AgentController) for task division or collaborative problem-solving.
- Secure Sandbox Execution: Code and commands run in isolated environments (e.g., Docker containers) to ensure safety and minimize risks to the host system.
Use Cases:
- Assisting developers with routine coding tasks
- Automating testing and deployment pipelines
- Rapid prototyping and tool development
No.5: MetaGPT
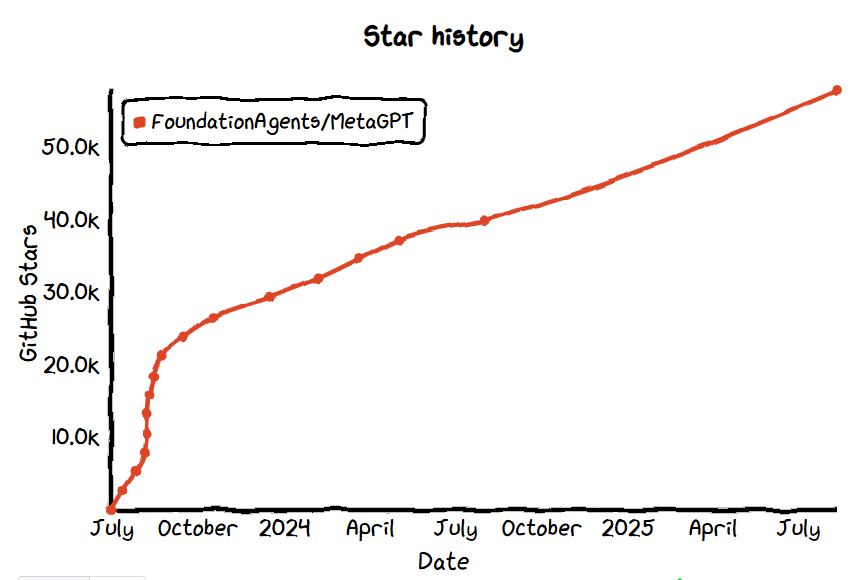
- GitHub Star: 57.8k
- GitHub: https://github.com/FoundationAgents/MetaGPT
- Website: https://mgx.dev/
Overview:
MetaGPT is a multi-agent collaboration framework inspired by the concept of simulating a “software company.” It transforms natural language requirements into a complete workflow — from user stories and competitive analysis to API design and documentation. Its core philosophy is “Code = SOP(Team),” turning standard operating procedures (SOPs) into actionable steps across roles like product managers, architects, and engineers.
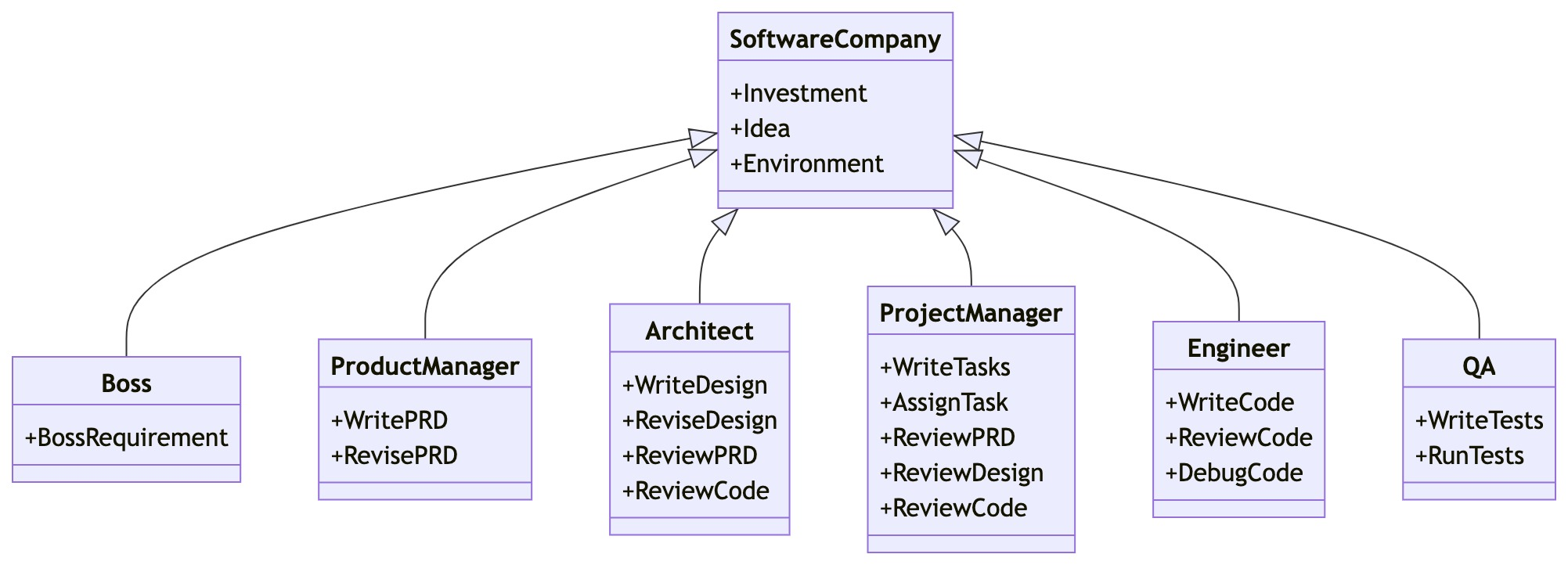
Core Features:
- Multi-Role Agent Collaboration: Includes built-in agents for roles such as product manager, architect, project manager, and engineer, simulating a real-world team executing SOP-driven projects.
- SOP-Driven Processes: Guides each agent with standard operating procedures for task breakdown, structured execution, and reduced deviation or hallucination.
- Natural Language Programming: Users can describe their requirements in plain language, and MetaGPT will generate corresponding user stories, data structures, API interfaces, and architecture designs.
Use Cases:
- Automatically generating software project proposals
- Rapidly prototyping collaborative team workflows
- Exploring AI-driven software development optimization and automation
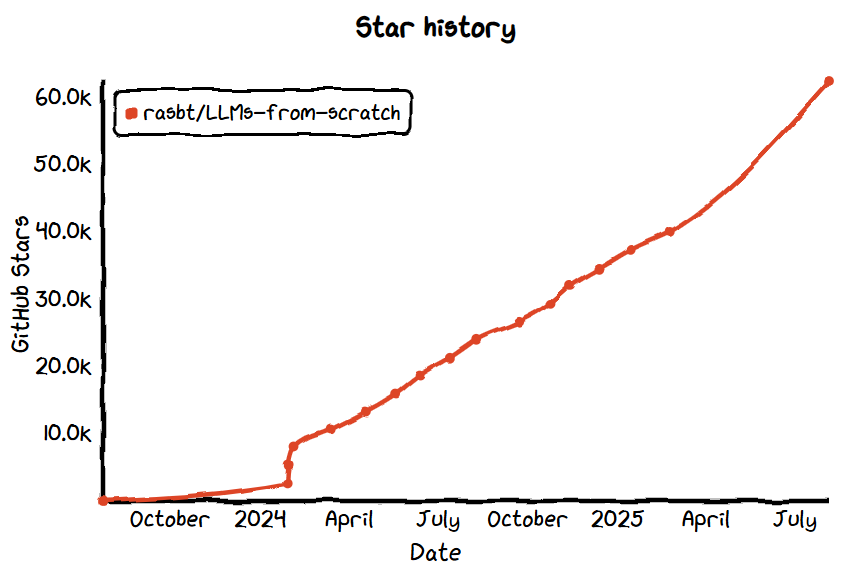
No.6: LLMs-from-scratch
- GitHub Star: 56k
- GitHub: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
Overview:
LLMs-from-scratch is an educational project that builds a large language model from the ground up, helping developers understand the core principles and training process of LLMs.
👉 See the full introduction and use cases for more details.
No.7: Huginn

- GitHub Star: 47k
- GitHub: https://github.com/huginn/huginn
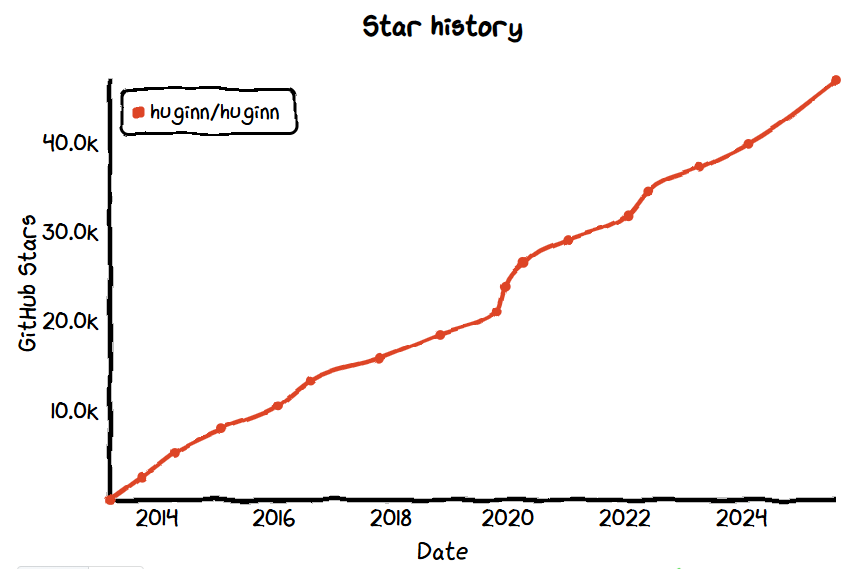
Overview:
Huginn is an open-source automation tool that allows users to run agents on their own servers to collect information from the web and trigger actions based on conditions — such as sending email notifications or monitoring keywords. Designed with data control in mind, Huginn has maintained long-term community activity thanks to its self-hosted, privacy-friendly, and extensible agent system.
Core Features:
- Self-Hosted Web Agent Platform: Users deploy agents on their own servers, process data autonomously, and ensure full privacy and control.
- Event–Action Rules Engine: Supports conditional triggers that automatically execute actions like sending notifications, running scripts, or making HTTP calls when specific web events occur.
- Extensible Agent Mechanism: Comes with many built-in agents and supports adding custom agents via Huginn Agent gems.
Use Cases:
- Information monitoring and alerts
- Data scraping and automated workflows
- Building custom automation tools
No.8: Unsloth
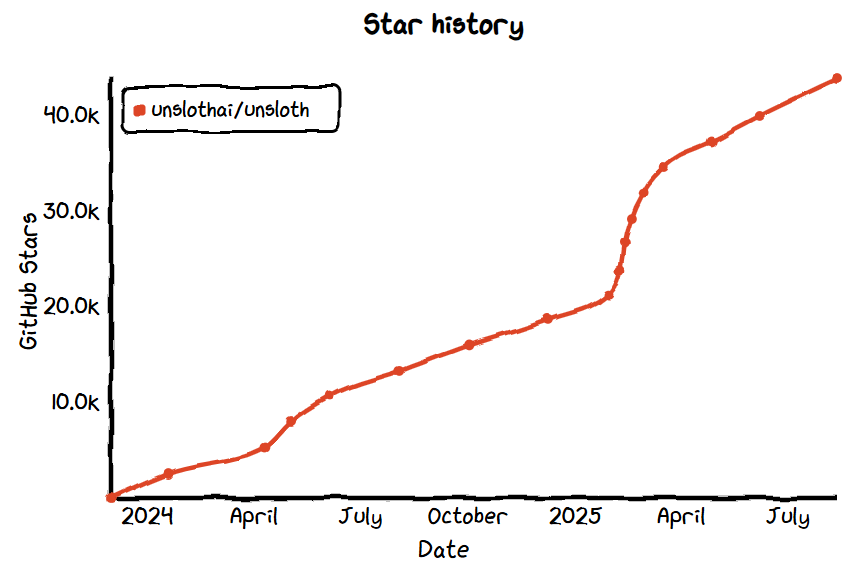
- GitHub Star: 43.8k
- GitHub: https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth
- Website: https://docs.unsloth.ai/
Overview:
Unsloth is an open-source toolkit designed for fine-tuning LLMs (such as OpenAI gpt-oss, Qwen3, Llama 4) with a focus on higher efficiency and memory optimization. Built on OpenAI’s Triton architecture, it significantly accelerates training speed while reducing GPU memory usage.
Core Features:
- Memory-Optimized Fine-Tuning: Delivers a 1.5–2.2× speed boost for fine-tuning mainstream LLMs while reducing GPU memory usage by up to 70–80%.
- Easy Notebook Workflow: Users simply add a dataset and click “Run All” to complete model fine-tuning quickly.
- Broad Model Compatibility: Supports fine-tuning LLMs including Llama, Gemma, Qwen, and more.
Use Cases:
- Rapidly fine-tuning LLMs for research or product prototyping
- Education and training
- Scenarios requiring high memory efficiency, such as deployment on resource-limited devices
No.9: Mem0
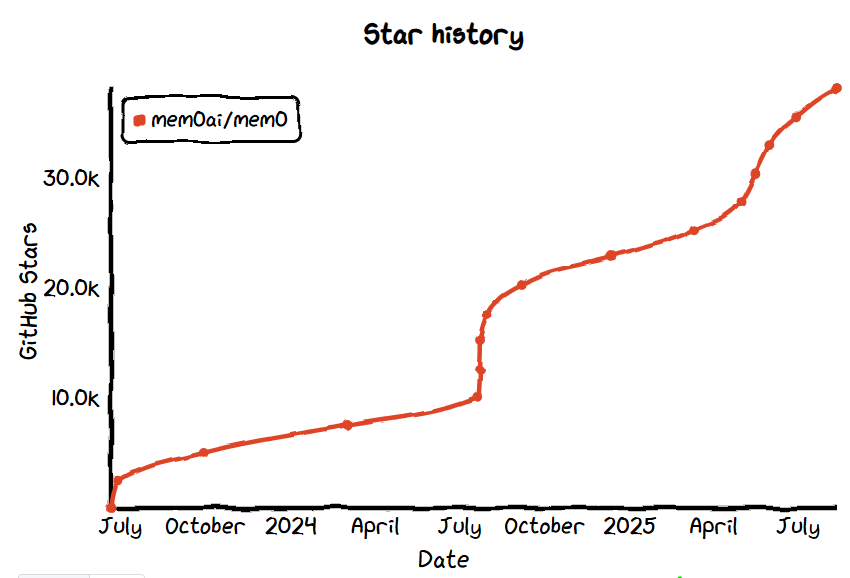
- GitHub Star: 38.1k
- GitHub: https://github.com/mem0ai/mem0
- Website: https://mem0.ai/
Overview:
Mem0 is a long-term memory management system purpose-built for AI agents, addressing the common issue of “forgetfulness” in AI. By introducing a unified memory layer, it allows agents to persist user preferences and historical context across sessions and applications, enabling personalized and continuous interactions.
In LOCOMO benchmark tests, Mem0 outperformed OpenAI Memory with around 26% higher accuracy, 91% lower response latency, and 90% lower token usage. It’s ideal for scenarios like customer service bots, AI assistants, and autonomous systems where context continuity is essential.
Core Features:
- Multi-Level Memory Architecture: Supports user-level, session-level, and agent-level memory layers for structured information storage.
- High Performance & Cost Efficiency: Improves accuracy while significantly reducing latency and token consumption, delivering long-term memory support with fewer resources.
- Privacy-First Local Processing: All data can be processed and stored locally, giving users complete control over their information.
Use Cases:
- Customer Service Bots: Retain user preferences and history to improve response relevance
- AI Assistants: Maintain task and persona memory across sessions for more natural, coherent interactions
- Medical & Counseling Systems: Preserve context to enhance service quality and precision feedback
No.10: ChatTTS

- GitHub Star: 37.5k
- GitHub: https://github.com/2noise/ChatTTS
- Website: https://2noise.com/
Overview:
ChatTTS is an open-source text-to-speech system optimized specifically for conversational tasks, supporting multi-speaker scenarios with a focus on natural, emotionally rich expression. To prevent misuse, the project incorporates a small amount of high-frequency noise into the trained model and reduces file quality, with plans to implement detection mechanisms to further guide ethical use.
Key Features:
- Conversation-optimized TTS: Specially tuned for dialogue scenarios, supporting multi-role conversations and natural pacing.
- Fine-grained prosody control: Precisely manages prosodic elements like laughter, pauses, and filler words, making synthesized speech more vivid and lifelike.
Core Features:
- Building human-like voice bots or interactive dialogue systems.
- Character dubbing and language practice tools in educational products.
- Audio assistance for voice content creation and automated podcast generation.
No.11: Arthas

- GitHub Star: 36.6k
- GitHub: https://github.com/alibaba/arthas
- Website: https://arthas.aliyun.com/
Overview:
Arthas is an open-source Java diagnostic tool from Alibaba, and since its release, it has become a go-to solution for Java developers troubleshooting production environment issues. Designed to attach dynamically to production applications without modifying code or restarting servers, it allows developers to run debugging commands, inspect stack traces, or set breakpoints, greatly improving efficiency and safety in production issue resolution.
Core Features:
- Dynamic attach execution: Inject Arthas into a running production JVM app without restarts or code changes to start debugging and monitoring instantly.
- CLI-based interactive diagnostics: Provides commands like
stack,trace,watch, andmonitorto instantly view runtime stacks, method call counts, performance metrics, and more.
Use Cases:
- Rapid production incident resolution.
- Performance bottleneck analysis.
- Regression testing issue investigation.
No.12: AgentGPT
- GitHub Star: 34.7k
- GitHub: https://github.com/reworkd/AgentGPT
- Website: https://arthas.aliyun.com/
Overview:
AgentGPT is an open-source project that allows users to configure and deploy AI agents directly in the browser without complex setup. With a user-friendly interface, simply input a goal, and the agent will “think–act–learn” to accomplish it.
Core Features:
- Browser-based agent configuration: Set goals and names directly in the web interface to launch agents, lowering deployment barriers.
- Goal-driven execution: Agents autonomously plan sub-tasks, execute them, provide feedback, and optimize their approach.
- Automated environment setup: Built-in CLI configures environment variables, database (MySQL), backend (FastAPI), and frontend (Next.js) for one-click deployment.
Use Cases:
- Task-focused intelligent assistants.
- Prototype validation tools.
- Learning and demonstration platforms.
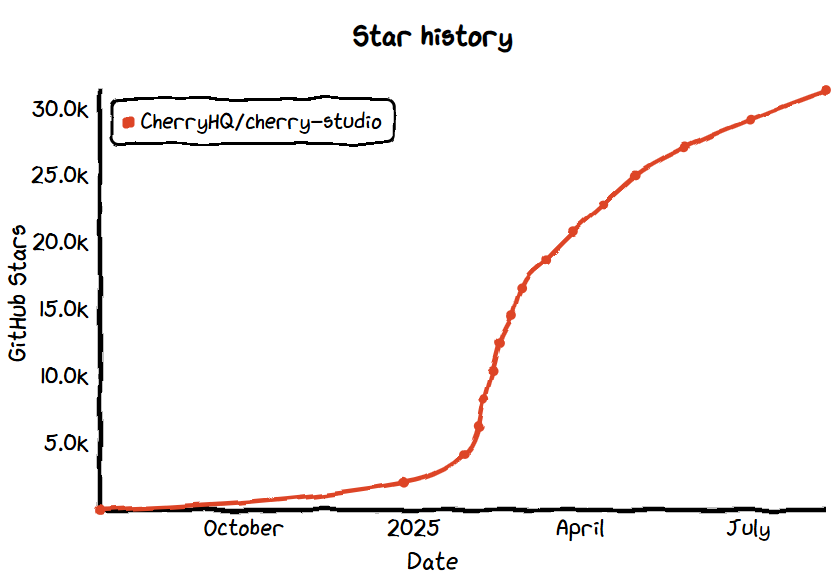
No.13: Cherry Studio
- GitHub Star: 31.3k
- GitHub: https://github.com/CherryHQ/cherry-studio
- Website: https://cherry-ai.com/
Overview:
Cherry Studio, launched in December 2024, is a joint AI coding assistant platform by CSDN, GitCode, and Huawei Cloud CodeArts IDE. It aims to provide a one-stop matrix of AI assistants for developers, supporting natural language interaction, project-level code refactoring, and full-stack development support.
Core Features:
- AI assistant matrix: Includes 300+ industry-specific AI assistant templates, with the option to create custom ones, covering areas from writing to programming.
- Multi-model aggregation: Freely switch between cloud models like OpenAI and Gemini or local models, and compare outputs from multiple models in parallel.
- Visual agent editing: Choose from preset assistants in the “Agent Marketplace” or create custom agents, with AI-assisted prompt optimization.
Use Cases:
- Project-level code assistance.
- Industry-specific solutions.
- Knowledge-driven code generation.
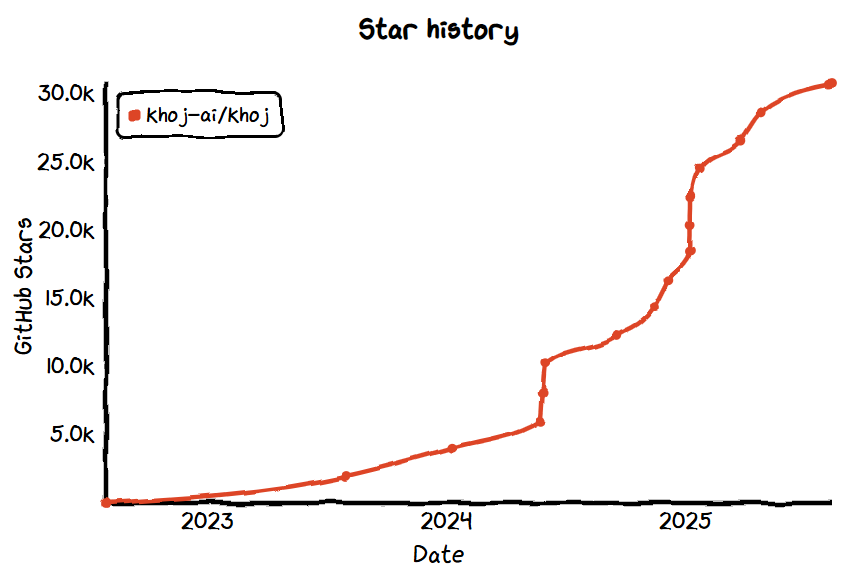
No.14: Khoj
- GitHub Star: 31.3k
- GitHub: https://github.com/khoj-ai/khoj
- Website: https://khoj.dev/
Overview:
Khoj is an open-source personal “second brain” assistant that integrates documents from multiple sources into a knowledge base, enabling semantic search for Q&A and intelligent reminders. It supports creating custom agents for scheduled tasks, content delivery, or real-time conversational responses.
Core Features:
- Multi-source knowledge integration: Imports content from PDF, Markdown, Notion, GitHub, and more into a unified knowledge base.
- Semantic search and notifications: Retrieves document content using natural language queries, with scheduled push notifications and email reminders.
- Cross-platform agent support: Works on desktop, as an Obsidian plugin, web, Emacs, WhatsApp, and more.
Use Cases:
- Personal knowledge management assistant.
- Automated reminder systems.
- Cross-tool integration experiences.
No.15: AIHawk

- GitHub Star: 28.6k
- GitHub: https://github.com/feder-cr/Jobs\_Applier\_AI\_Agent\_AIHawk
- Website: https://laboro.co/
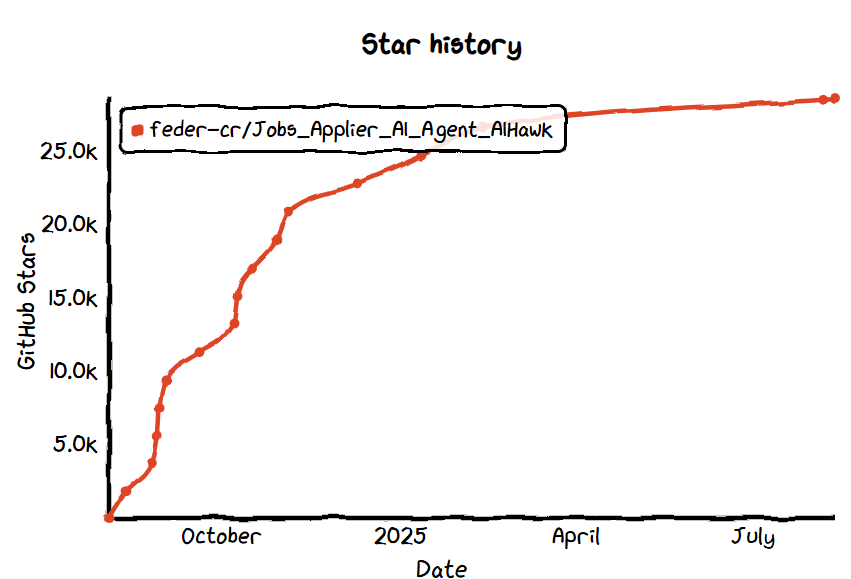
Overview:
AIHawk is an AGPL-licensed open-source AI agent focused on automating job applications. It scrapes job listings and uses language models to generate tailored application materials, helping users apply efficiently.
Core Features:
- Automated job applications: Crawls job websites and generates optimized application materials.
- Extensible open-source architecture: Developers can customize behavior or add plugins.
- Commercial platform extension: Evolved into the laboro.co platform, offering hosted services and expanded recruitment automation features.
Use Cases:
- Automatic job application assistant.
- Recruitment process automation research.
- Recruitment platform integration tools.
No.16: FastGPT

- GitHub Star: 25.5k
- GitHub: https://github.com/labring/FastGPT
- Website: https://fastgpt.io/
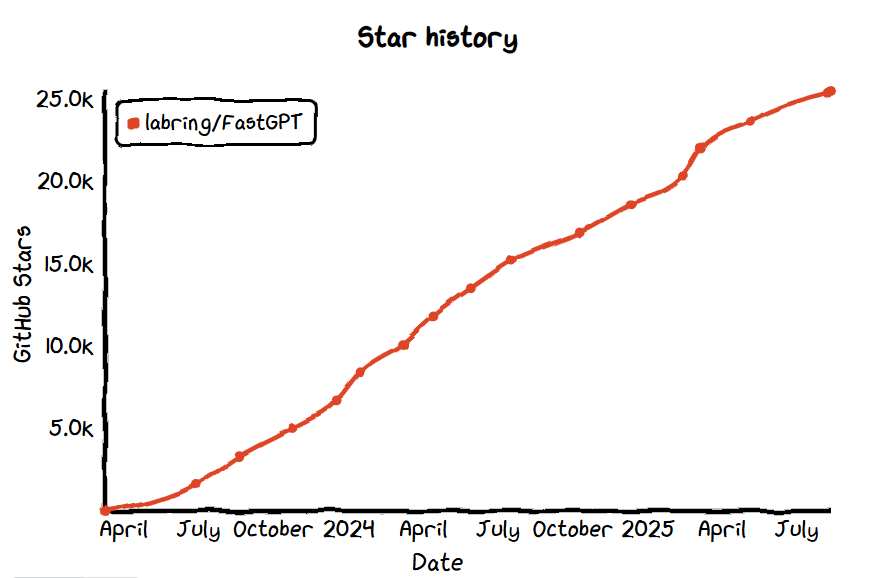
Overview:
FastGPT is designed as an “AI agent building platform,” enabling developers to construct complex AI applications using visual workflows and knowledge bases, without tedious configuration.
Core Features:
- Visual workflow orchestration: Drag-and-drop interface supporting dialogue nodes, HTTP calls, RPA, conditional branches, and more.
- Knowledge base & RAG support: Import multiple file formats (txt, md, pdf, etc.), with vector and hybrid retrieval for knowledge-driven Q&A and automation.
- Multi-model & API compatibility: Integrates with OpenAI, Claude, and others; provides OpenAPI-compatible interfaces for easy embedding into existing systems.
Use Cases:
- Rapidly building intelligent Q&A bots (e.g., customer service assistants).
- Document analysis and automated summarization workflows.
- Automated task handling with external API integration.
No.17: GPT Researcher
- GitHub Star: 22.9k
- GitHub: https://github.com/assafelovic/gpt-researcher
- Website: https://gptr.dev/
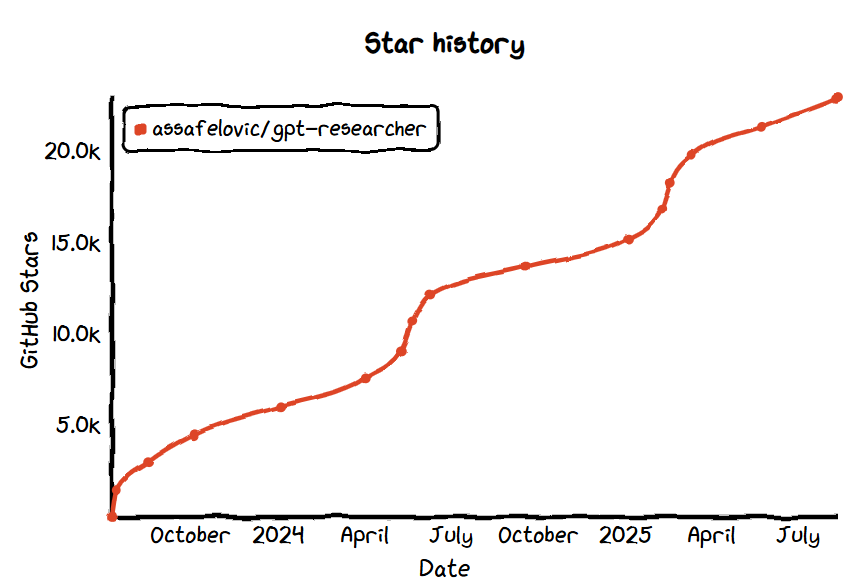
Overview:
GPT Researcher is an AI agent framework specialized for deep research tasks. It can automatically plan research workflows, scrape information, generate research reports, and output content with citations, offering high report quality and customizability.
Core Features:
- Parallel agent research: A planner agent creates research questions, while multiple executor agents gather and summarize information in parallel for greater efficiency and reliability.
- Factual report generation: Organizes and cites content automatically, producing structured, objective research reports with sources.
Use Cases:
- Writing competitive analysis or technical research reports quickly.
- Automated creation of academic research outlines or background summaries.
- Building domain-specific knowledge agents for enterprise knowledge aggregation.
No.18: CopilotKit
- GitHub Star: 22.4k
- GitHub: https://github.com/CopilotKit/CopilotKit
- Website: https://docs.copilotkit.ai/
Overview:
CopilotKit is an open-source framework for seamlessly integrating AI copilots into applications—whether as embedded chat, intelligent text areas, or full agent interfaces. It provides React UI components and a headless architecture for flexible embedding.
Core Features:
- React & headless UI support: Plug-and-play UI components or headless API-only deployments.
- Application context integration: Connects app logic, state, and user context to AI agents for more tailored functionality.
- Model-architecture decoupling: Works independently of specific models or agent frameworks, allowing AI stack upgrades without affecting user experience.
Use Cases:
- Embedded AI assistants.
- Custom AI tools.
- Multi-modal interactive experiences.
Final Note
Agents excel at exploration but struggle with strict rule-following.
The 18 open-source agent projects above are both a toolbox and a reminder: selecting the right scenarios and designing reasonable boundaries is key to maximizing the value of agents.
If this article inspired you, feel free to share it with others exploring AI agents. 👍
Related reading:
- Top 20 Open Source AI Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 8 Open Source MCP Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 7 Open Source Web Applications with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 40 Open-source Developer Tools with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 15 Fastest-Growing Open-Source Low-Code Projects on GitHub in 2025
- Top 11 Open-source CRM Projects with the Most GitHub Stars