📝 Note: This article was last updated on Jan. 21, 2026. We regularly update the information to ensure you have the latest insights! 😊
The term MCP truly gained widespread attention in early 2025, especially within the AI tool development community.
In March, a heated debate about “MCP - flash in the pan or future standard?” ignited the discussion. Core members from LangChain and LangGraph clashed intensely on X, and MCP-related projects on GitHub started trending one after another.
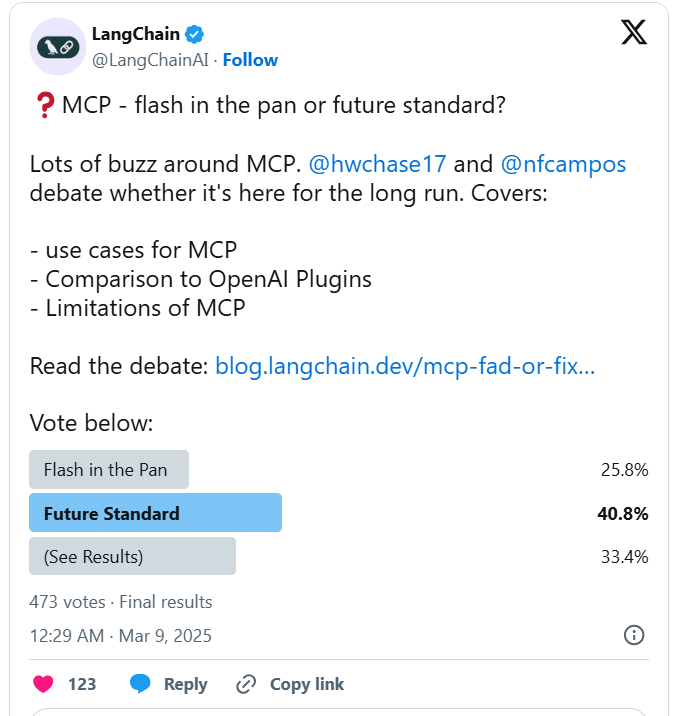
Image source: https://blog.langchain.com/mcp-fad-or-fixture/
Why is MCP gaining popularity?
At its core, developers have finally realized this: ChatGPT can generate content but can’t automatically fetch web pages; Claude can understand PDFs but cannot call APIs. Although the models are powerful, they lack a closed execution loop, and tool integration remains a bottleneck.
MCP aims to solve this“last mile”problem. It acts like a USB-C port for models, helping AI unify access to browsers, databases, plugin systems, and more, enabling models not just to talk but to take action.
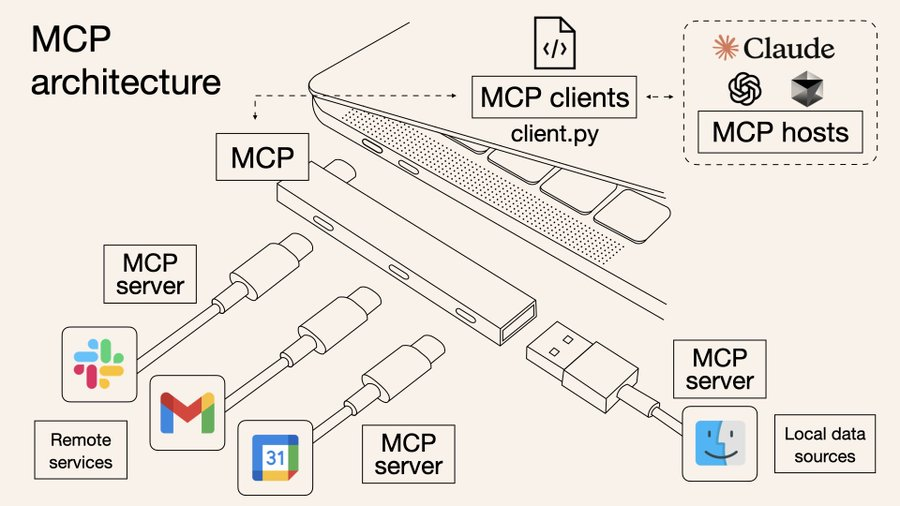
Image source: https://norahsakal.com/blog/mcp-vs-api-model-context-protocol-explained/
We continuously track quality open-source projects on GitHub and found many tools inspired by the MCP concept trying to solve these issues. Some focus on automation workflows, others on plugin extensions, and some explore multi-model collaboration.
This article summarizes the top 8 most popular MCP projects on GitHub, briefly analyzing their introductions, core features, deployment and integration methods, and application scenarios for your practical reference.
💡 Also welcome to check our previous popular GitHub project series articles:
- Top 40 Open-source Developer Tools with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 15 Fastest-Growing Open-Source Low-Code Projects on GitHub in 2025
- Top 7 Open Source Web Applications with the Most GitHub Stars
💬 Hey, you’re reading the NocoBase blog. NocoBase is the most extensible AI-powered no-code/low-code development platform for building enterprise applications, internal tools, and all kinds of systems. It’s fully self-hosted, plugin-based, and developer-friendly. → Explore NocoBase on GitHub
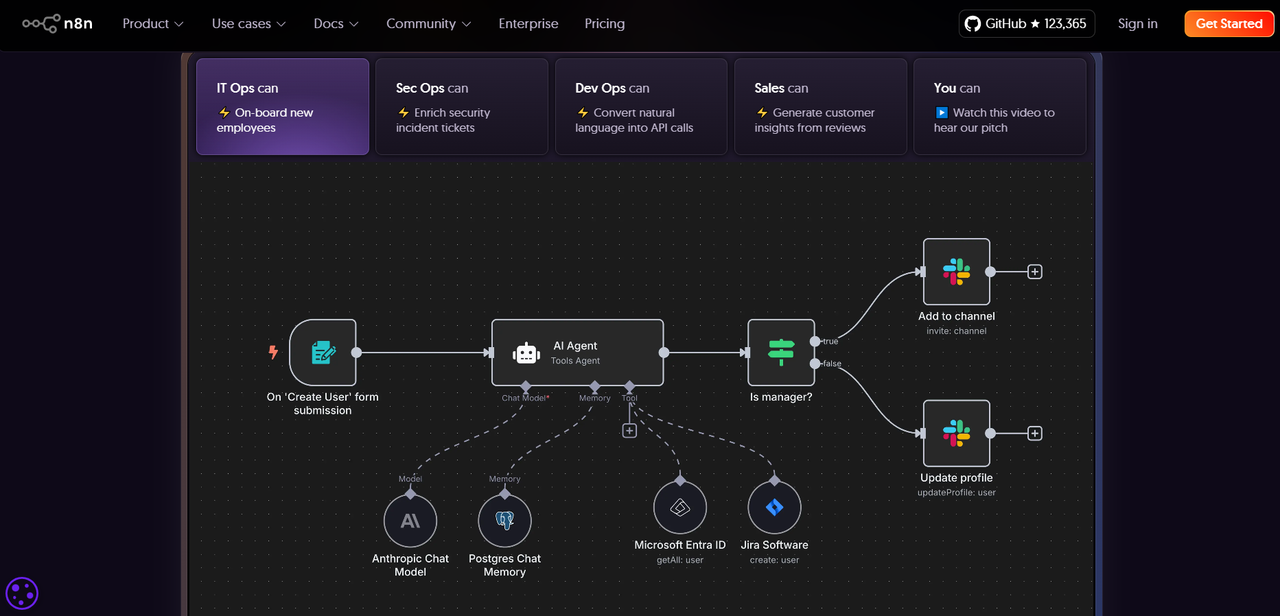
No.1: n8n
GitHub Star: 124k
GitHub: https://github.com/n8n-io/n8n
Website: https://n8n.io/
Introduction:
In the past year, n8n quickly rose from a niche open-source automation tool to widespread popularity. Initially positioned as an open-source alternative to platforms like Zapier and Make, it supports visually connecting various APIs and services with far greater flexibility than traditional automation tools.
But n8n is much more than that. Its explosive growth results from the combined demand for open-source, autonomy, and AI. With OpenAI, Hugging Face, and other models rapidly entering enterprise use, n8n has become an ideal choice for developers to build AI invocation chains, intelligent agents, and business assistants. It can easily integrate third-party model services and embed AI into business workflows through custom logic, driving practical intelligent automation.
Core features:
- Visual workflow builder: Build automation execution chains by dragging and connecting nodes.
- Webhook and API support: Built-in webhook nodes receive structured requests from AI agents; API nodes send requests to external systems.
- Logic and data processing: Function nodes enable conditional logic, loops, and data transformation for flexible task control.
Deployment and integration:
- Flexible deployment: Supports local operation, Docker, one-click installation, and cloud deployment for personal or enterprise environments.
- Strong system integration: Over 500 built-in integrations including databases, third-party APIs, GPT, file services, etc.
What can you do with n8n?
- AI assistant calling external services: Type “Schedule a meeting for tomorrow afternoon” in the chat; n8n receives the request, extracts context, sends it to OpenAI, and upon intent recognition, automatically calls Google Calendar to create the event and returns confirmation.
- Enterprise knowledge base Q&A system: When asked “What payment methods does our product support?”, n8n queries an internal document vector database, extracts relevant content, constructs context, generates precise answers via the model, and replies via Slack.
- Auto-entry of model-generated content: Trigger GPT daily to summarize the previous day’s sales calls; n8n processes the response, extracts keywords, potential clients, next steps, writes into CRM, and posts a daily report summary in group chat.
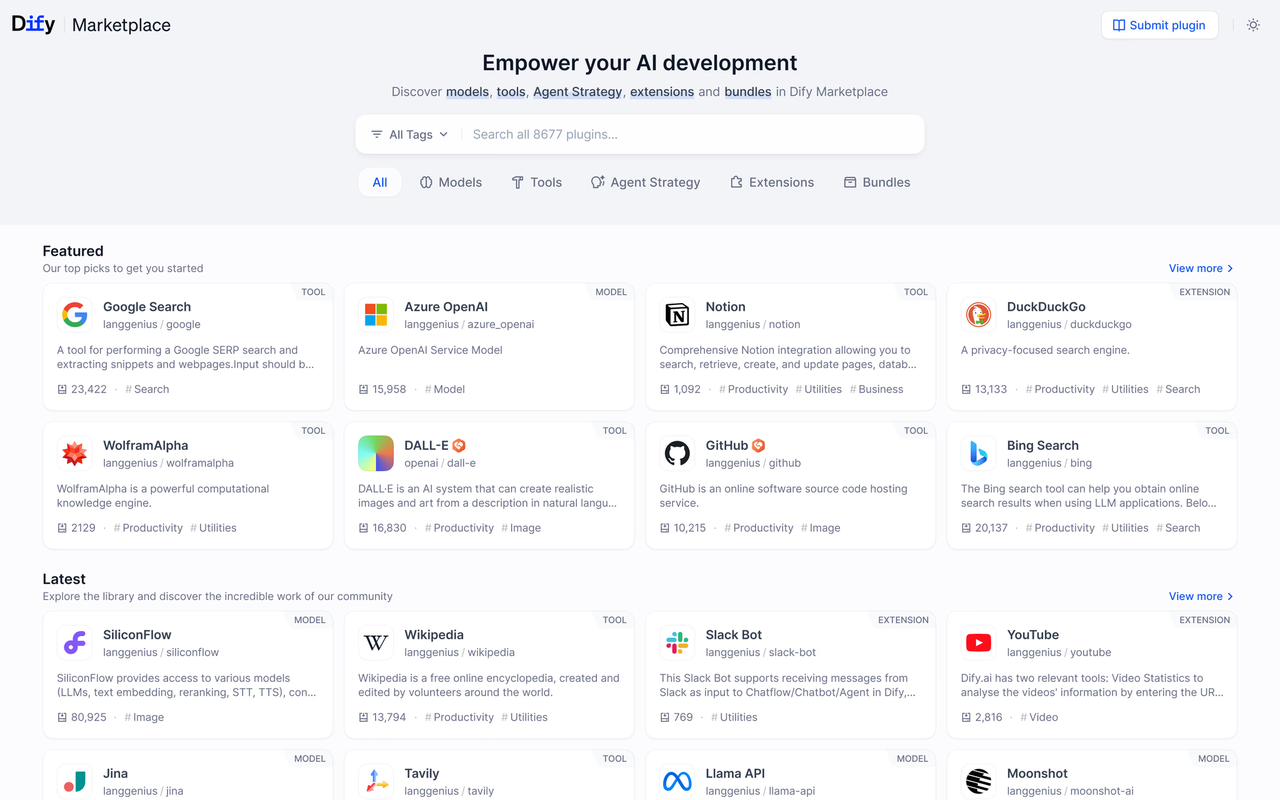
No.2: dify
GitHub Star: 109k
GitHub: https://github.com/langgenius/dify
Website: https://dify.ai/
Introduction:
Dify is another rapidly rising open-source AI application platform over the past year. Initially marketed as a “plug-and-play LLM application development framework,” it has evolved into an AI workspace supporting multiple models and application forms — enabling you to build chatbots, agent workflows, RAG systems, or AI copilots without starting from scratch.
Dify provides near “plug-and-play” solutions: supporting OpenAI, Claude, Gemini and other major models, complex context settings and variable inputs, with built-in datasets, workflows, and plugins — letting you build LLM applications as easily as low-code systems.
Core features:
- Bidirectional MCP support: Can connect to MCP servers or act as an MCP server, directly solving AI-system instruction interaction.
- Visual workflow builder: Drag-and-drop to create AI applications and workflows, making MCP task design intuitive and efficient.
- Multi-model and tool integration: Supports global large language models, plugin integration, and RAG pipelines to extend MCP task capabilities.
Deployment and integration: Supports Docker and AWS AMI one-click deployment, offers SaaS version, adapts to various scale environments, with API and Webhook interfaces.
What can you do with Dify?
- Internal intelligent assistant: Upload company documents, connect OpenAI or Claude, configure common questions and variables, quickly build a business-aware, memory-capable internal assistant. Frontend SDK and API allow embedding into your website or system with few lines of code.
- Build multi-turn RAG applications: Dify’s dataset management and context control enable quick vector search-based multi-turn dialog systems, no need to build vector stores or tune prompts. Upload data, configure models, build a memory-enabled Q&A for support, knowledge bases, or AI copilots.
- Orchestrate models and plugins via workflows: Use Dify workflows to chain multiple model calls, plugin executions, API requests — enabling complex agent logic like intent recognition → database query → result processing → user response in a visual interface.
No.3: Open WebUI
GitHub Star: 104k
GitHub: https://github.com/open-webui/open-webui
Website: https://openwebui.com/
Introduction:
Open WebUI is a local deployment-friendly LLM chat interface connecting seamlessly with OpenAI API, LM Studio, Ollama, and other backends. It is open-source, lightweight, supports multi-model switching, session context, multi-user support, and plugin systems. Think of it as a “plug-and-play ChatGPT frontend” or a starting point to build AI copilots.
Open WebUI is favored by developers and teams for its ease of deployment, good interaction experience, and extensibility for internal AI apps.
Core features:
- Multi-model and API integration: Supports Ollama and OpenAI-compatible APIs via unified interface for AI model requests.
- Plugin framework (Pipelines): Load custom Python logic or plugins for task pre/post-processing and tool invocation.
- Local and remote RAG support: Built-in inference engine supports local document extraction, remote web integration, and RAG pipeline construction for contextual AI tasks.
Deployment and integration: Offers Docker and Kubernetes deployment, suitable for single-machine or enterprise clusters, supports REST API for model and plugin interface calls.
What can you do with Open WebUI?
- Deploy a private ChatGPT copy: Connect Open WebUI to locally deployed LLMs (e.g., Llama3, Mistral, Qwen) to use full ChatGPT features on LAN. Simple UI, context and multi-turn dialogue, one-click model switching—ideal for internal knowledge Q&A or work assistants.
- Build a developer team AI toolbox: Centralize model configuration, unify context templates, manage multi-user sessions with role settings. Deliver a style-aligned AI assistant to everyone, avoiding environment duplication.
- Use as an interactive frontend for LLM apps: Modify Open WebUI as a frontend shell connecting backend inference, databases, and business systems. Plugin mechanisms and API support allow handling Q&A, search, and command execution, making it a lightweight copilot facade.
No.4: Netdata
GitHub Star: 75.2k
GitHub: https://github.com/netdata/netdata
Website: https://www.netdata.cloud/
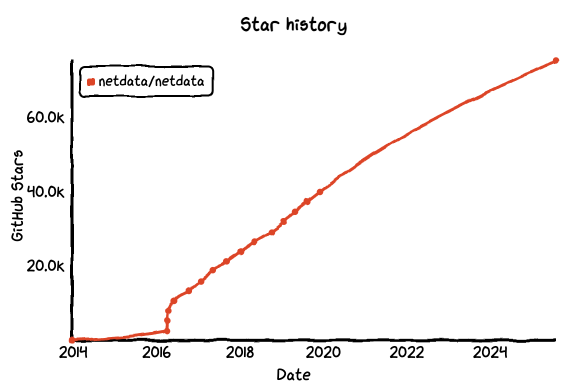
Introduction:
Netdata is an open-source, real-time system monitoring platform that provides insights into the performance of servers, containers, databases, and applications with near-zero configuration. Compared to traditional monitoring tools, it’s lightweight, incredibly responsive, and excels at high-frequency data collection and visualization.
As LLM deployments and agent workflows grow in complexity, Netdata is becoming a “core observability component” for many teams building MCP systems. You can use it not only to monitor infrastructure resources, but also to visualize inference latency, context size, call errors, and more — ensuring your entire task chain remains stable and debuggable.
Core features:
- MCP server capability: Netdata agents and the Cloud module function as MCP servers, enabling AI to interact directly with system monitoring data.
- Real-time monitoring & anomaly detection: Offers real-time performance metrics, logs, alerts, and automatic anomaly detection.
- AI-assisted operations chat: Supports querying infrastructure status via natural language, enabling AI-powered DevOps assistants.
Deployment and integration:
- Easy installation via Docker, package managers, or custom scripts across servers, containers, and cloud VMs.
- Over 800+ integrations with standard MCP interfaces; AI agents can query monitoring data in real-time.
What can you do with Netdata?
- Monitor local LLM resource usage in real time: Netdata can track GPU, CPU, memory, disk, and other key metrics at second-level granularity — ideal for ensuring local model deployments run smoothly.
- Build dashboards for AI workflows: Embed Netdata into inference services or agent pipelines to visualize API calls, response times, context usage, etc. You can even set up automatic alerts for failures like long model hang-ups or sudden error spikes.
- Give your AI system an observable “black box”: Netdata’s detailed call traces and historical graphs help recreate the exact environment where a failure occurred — whether it’s a broken RAG link, failed plugin call, or GPU throttling.
No.5: Lobe Chat
GitHub Star: 63.9k
GitHub: https://github.com/lobehub/lobe-chat
Website: https://lobechat.com/
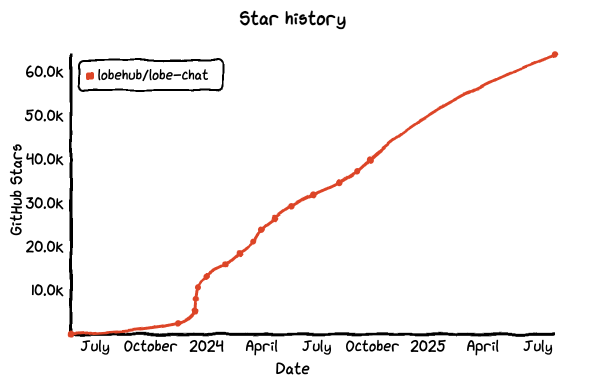
Introduction:
Lobe Chat is an open-source, visually polished, feature-rich LLM chat system. It supports multiple models, conversations, and plugins — fully compatible with OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, Ollama, and others. Compared to other tools, Lobe Chat emphasizes user experience and extensibility, offering advanced features like conversation variables, prompt templates, and role presets. It works well for both personal and team-oriented Copilot setups.
With the rise of MCP architectures in AI applications, Lobe Chat is becoming the “human interaction layer” for developers — a frontend hub for managing context-aware, multi-model, plugin-enabled experiences.
Core features:
- Multi-model & RAG support: Integrates OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, local models, and supports knowledge base search with context-aware responses.
- MCP plugin marketplace: Comes with a built-in MCP plugin store for importing tools and agent actions with one click.
- Function calling system: Supports cross-model external function execution via plugin protocols.
Deployment and integration: Deploy privately with one click via Docker, Vercel, and more. Easily embed into apps or integrate with external systems via API.
What can you do with Lobe Chat?
- Deploy your own multi-model assistant: Hook up Llama3, GPT-4, Claude, Qwen, etc. — switch between them seamlessly. Configure memory, roles, plugin calls. More flexible than ChatGPT, and fully private.
- Build an AI Copilot with plugin chains: Connect database APIs, search engines, or other tools via plugins. The assistant can process complex tasks like “import this spreadsheet to Notion and summarize” through automatic execution.
- Create shareable AI app frontends: Lobe Chat enables you to build lightweight, shareable prompt tools or agent workflows. Share links or embed in pages — ideal for internal tools or customer-facing micro-products.
No.6: Glama
GitHub Star: 63.6k
GitHub: https://github.com/punkpeye/awesome-mcp-servers
Website: https://glama.ai/mcp/servers
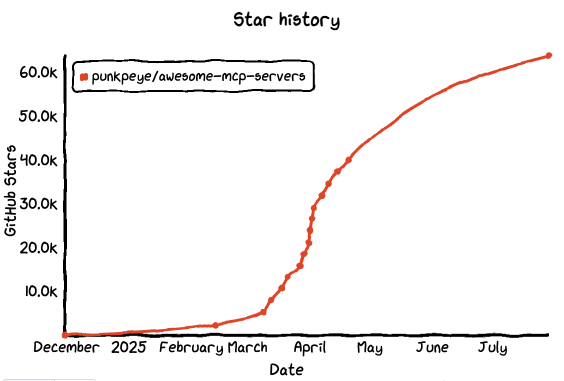
Introduction:
Unlike the previous tools, Glama is an open-source client built specifically for MCP protocols. It connects and interacts with multiple MCP-compatible services (like LobeChat, Open WebUI) in a single interface. It doesn’t run models itself — instead, it acts as an “aggregated frontend” where you can toggle between models, plugins, and context providers like switching tabs in ChatGPT.
Glama offers a new “modular experience” — pick any MCP-compatible backend, attach multiple plugin tools, even mix models from different vendors. For developers and AI engineers, it’s a unified window to observe, test, and orchestrate multiple AI services.
Core features:
- Rich MCP server aggregation: Includes Kong Konnect, Powerdrill, YingDao RPA, StarTree, and more — covering gateways, analytics, RPA, databases, and beyond.
- Standardized interaction layer: All servers follow the Model Context Protocol, ensuring unified formats for agent instructions.
- Targeted resource search: Quickly find tools and services via keyword search to match your use case.
Deployment and integration: Available as a web app with API access. Enterprise users can integrate directly into business systems or databases, receive task instructions via MCP.
What can you do with Glama?
- Centralized MCP service dashboard: Connect to multiple chat apps (LobeChat, Open WebUI) and plugin servers (AI-Plugin Server), then switch between them with shared context and UX.
- Test agent + plugin interaction: Quickly verify how different backends handle plugin calls. For example, see if a database plugin runs consistently across models or test response variations to optimize behavior.
- Prototype AI Copilot products: Use Glama to mock up the frontend for an AI product — model selector on the left, chat in the middle, plugin logs on the right. A working MCP loop in minutes.
No.7: RAGFlow
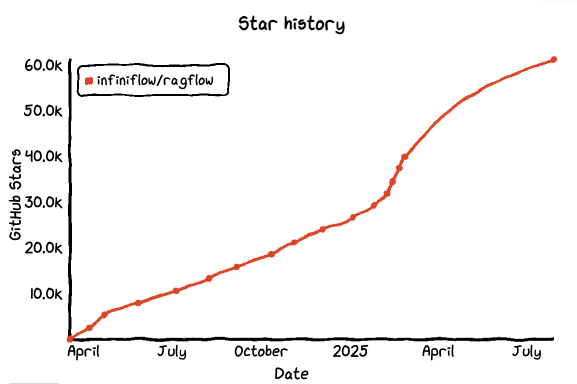
GitHub Star: 61.1k
GitHub: https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow
Website: https://ragflow.io/
Introduction:
RAGFlow, from the infiniflow team, is an open-source framework for building Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It emphasizes engineering qualities like modular pipeline design, decoupled retrieval/generation, and context chain visibility/debugging. Think of it as a pipeline tool for building stable, traceable, and production-grade knowledge Q&A systems.
Unlike general frameworks like LangChain or LlamaIndex, RAGFlow focuses more on “backend infrastructure” — targeting reproducibility, testability, and observability for enterprise-level use.
Core features:
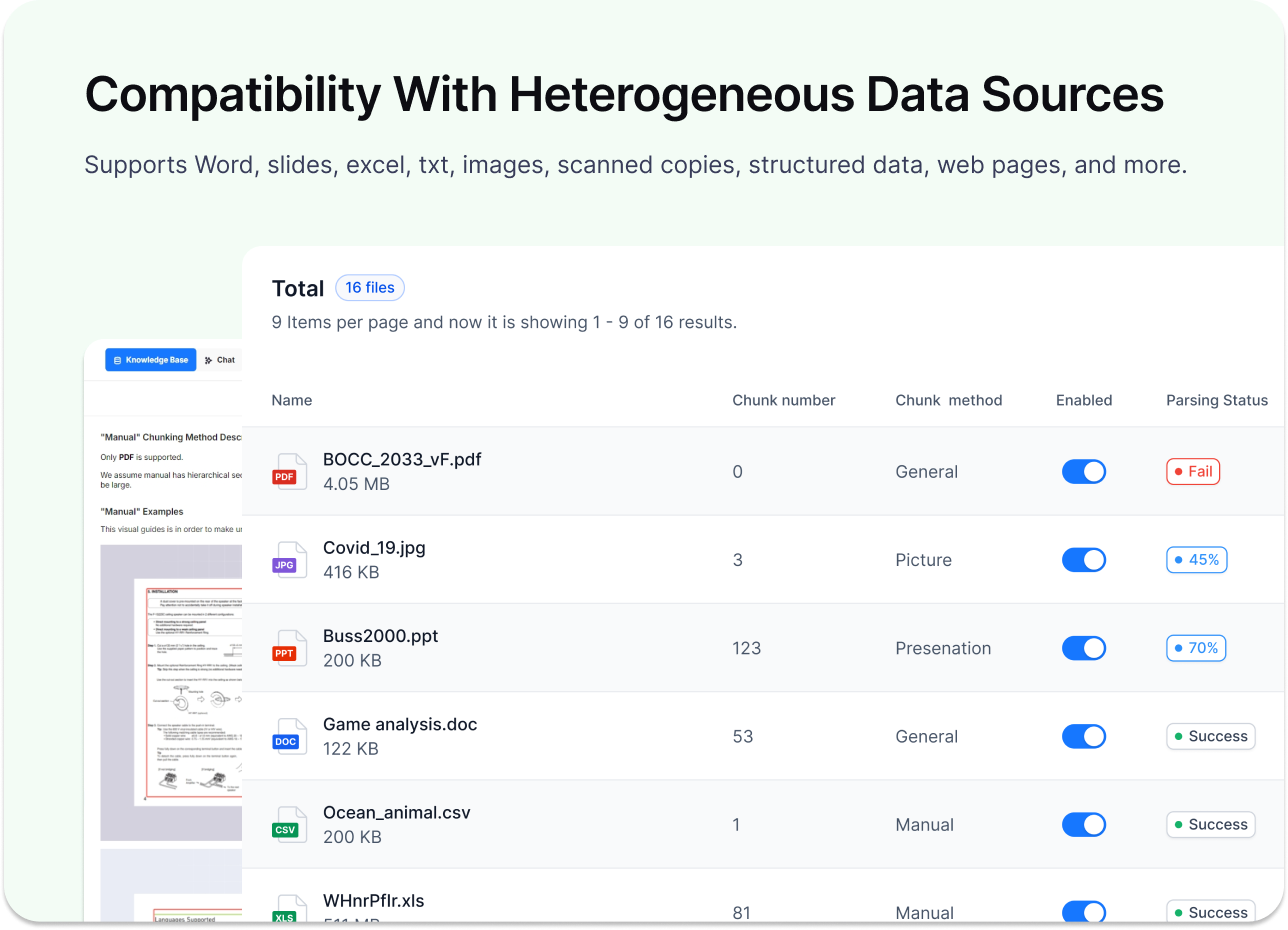
- Deep document parsing: Handles complex formats (multi-format files, structured content) and extracts high-quality context for LLMs.
- Knowledge base management: Create and manage internal knowledge repositories with parsing and storage capabilities.
- RAG generation with citation: Generates answers grounded in retrieved knowledge, with reference support.
Deployment and integration: Available via Docker Compose. Easily integrates with external LLMs.
What can you do with RAGFlow?
- Build modular enterprise Q&A systems: Configure every step — from document preprocessing to embedding and indexing — using replaceable components. Tailor the pipeline to match your business.
- Debug RAG chains effectively: Pinpoint why a RAG system failed — was it the retrieval? A context overflow? RAGFlow’s visual trace tools help isolate and fix issues quickly.
- Combine RAG with agent workflows: Integrate RAGFlow into larger agent systems (e.g. via Dify or Lobe Chat) using APIs or plugins to build intent detection → retrieval → response loops. Perfect for finance assistants, support agents, etc.
No.8: AnythingLLM

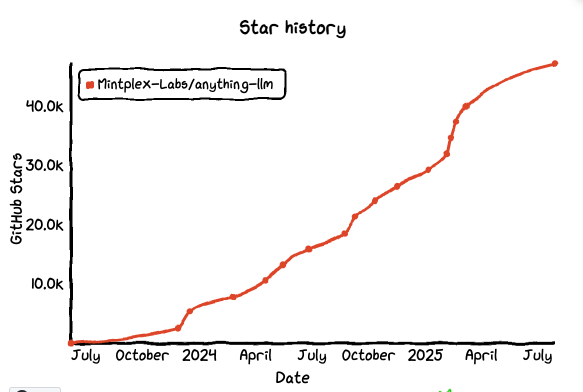
GitHub Star: 47.1k
GitHub: https://github.com/Mintplex-Labs/anything-llm
Website: https://anythingllm.com/
Introduction:
AnythingLLM is a full-stack open-source app for desktop and Docker deployment. It combines RAG, AI agents, visual/no-code agent pipelines, and native MCP compatibility. It supports multiple models and local/cloud vector stores, provides multi-user access, and can be embedded — great for private and team use cases.
Core features:
- Model + document interaction: Run local models or connect to OpenAI/Azure; process PDFs, Word docs, CSVs, and more.
- Custom agent skills with MCP: Extend agent capabilities with “skills” and integrate automated tool actions via MCP.
- Private, local-first architecture: All LLM, vector, and storage components run locally by default. Full control over data and execution.
Deployment and integration: Available as a desktop app or via Docker. Offers developer APIs for product integration.
What can you do with AnythingLLM?
- Build a private ChatGPT + knowledge base: Drag PDFs and websites into Workspaces. The system embeds, indexes, and responds with citations — cloud or local, you stay in control.
- Run agent + MCP toolchains: Configure an MCP server in the UI and let the agent call external tools — for fetching data, scraping, database ops — all in a closed loop with no code.
- Mix models and vector DBs flexibly: Use OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, or local Ollama. Choose from LanceDB, PGVector, Pinecone, Milvus, Qdrant. Embed the chat component in your frontend for full-stack delivery.
Conclusion
In just a few months, MCP has gone from a niche concept to a hot topic among developers. The standard is still evolving, and tools are still maturing — but more and more projects are proving that AI shouldn’t just talk, it should act.
For developers working on AI integration and automation, MCP offers a new perspective: intelligence alone isn’t enough. True value comes when AI can connect to real-world systems and drive meaningful action.
Hopefully, this guide gives you a useful snapshot of the emerging ecosystem — and maybe sparks ideas for your next AI build.
Related reading:
- Top 7 Open Source Web Applications with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 40 Open-source Developer Tools with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 15 Fastest-Growing Open-Source Low-Code Projects on GitHub in 2025
- Top 11 Open-source CRM Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
- Top 11 Open-Source Admin Dashboard Projects on GitHub
- Top 10 Open-source Workflows Projects with the Most GitHub Stars