📝 Note: This article was last updated on Jan. 21, 2026. We regularly update the information to ensure you have the latest insights! 😊
After the release of our previous article “Top 11 Open-Source Admin Dashboard Projects on GitHub”, a reader left a comment asking:
“How to evaluate the extensibility and customization capabilities of open-source Admin Dashboard projects to ensure they can adapt to the evolving business needs of enterprises?”
This is a core issue faced by many technical teams when selecting a solution. If a backend system cannot be flexibly extended or customized, it often becomes a bottleneck for business growth.
Overview of 6 Key Evaluation Dimensions
To evaluate the extensibility and customization capabilities of an open-source backend system, focus on the following six dimensions:
| Dimension | Key Focus Points |
|---|---|
| Interface Capability | Whether it is easy to integrate with external systems |
| Data Modeling Capability | Whether it supports flexible configuration and quick adjustment |
| Plugin Architecture | Whether it allows modular extension of functions |
| Automation & Workflow | Whether it can respond to changes in business processes |
| Permission Control | Whether it supports fine-grained role-based and data-level access control |
| UI Customization | Whether it supports interface customization and component extension |
💬 Hey, you’re reading the NocoBase blog. NocoBase is the most extensible AI-powered no-code/low-code development platform for building enterprise applications, internal tools, and all kinds of systems. It’s fully self-hosted, plugin-based, and developer-friendly. → Explore NocoBase on GitHub
Detailed Explanation of the Six Dimensions
1. Interface Capabilities
APIs serve as the bridge between the system and the external world. A highly scalable backend project should support standard API interfaces and allow developers to register custom interfaces or middleware, enabling flexible integration with various third-party systems or in-house services. The lack of interface extension capabilities often makes system integration difficult and restricts business development.
✅ Example: NocoBase supports plugin-level API registration, enabling flexible connection to external systems.
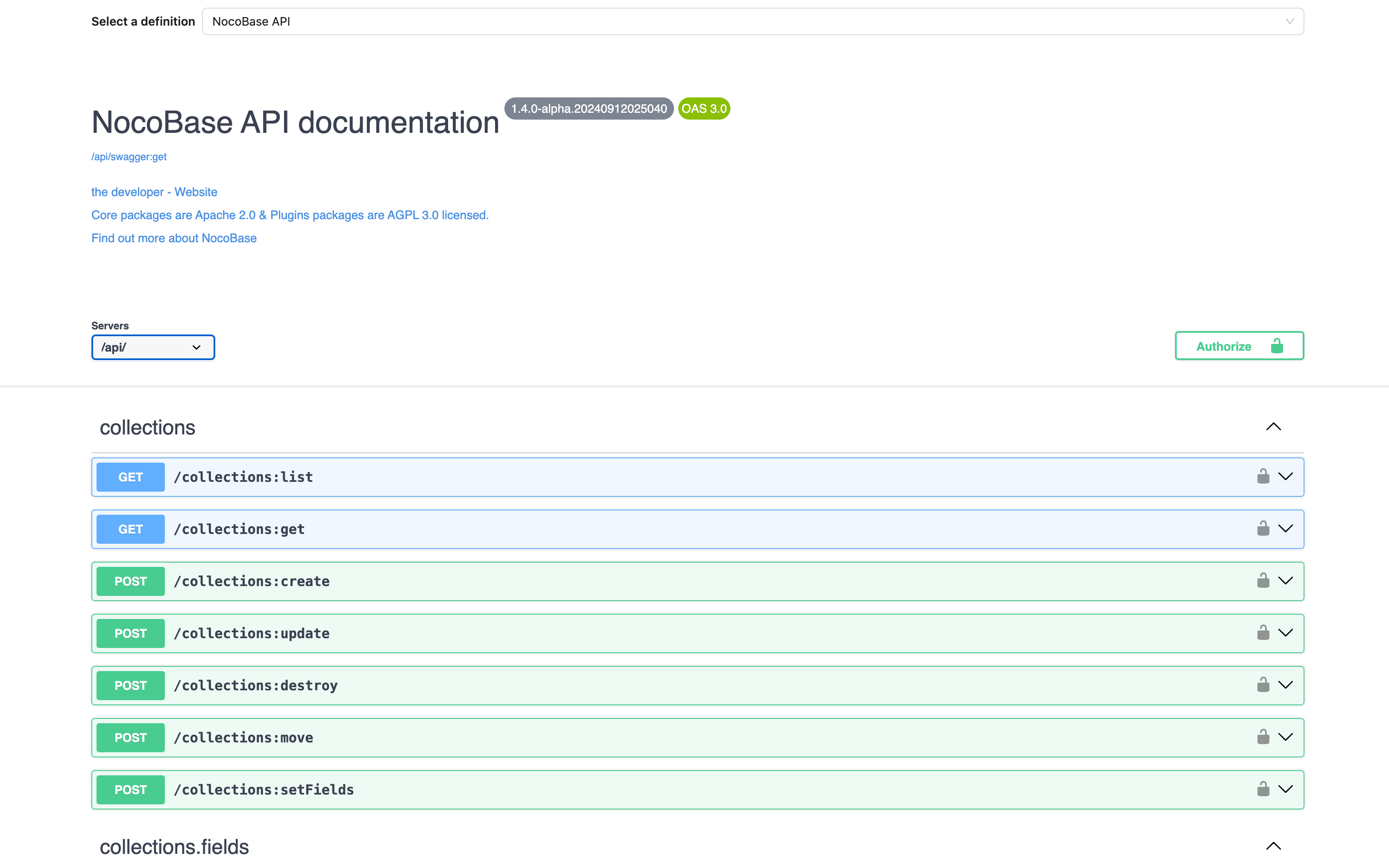
2. Data Modeling Capabilities
Business requirements are constantly evolving, and static, hard-coded data structures struggle to support long-term growth. An ideal backend system should allow flexible definition of field types, table relationships, and complex data structures through a graphical interface or configuration files, even supporting multi-level nested relationships. The more abstract and configurable the data model, the stronger the system’s ability to adapt to business changes.
✅ xample: NocoBase adopts a data model-driven approach, separating the user interface from the data structure, freeing development capabilities from limitations.
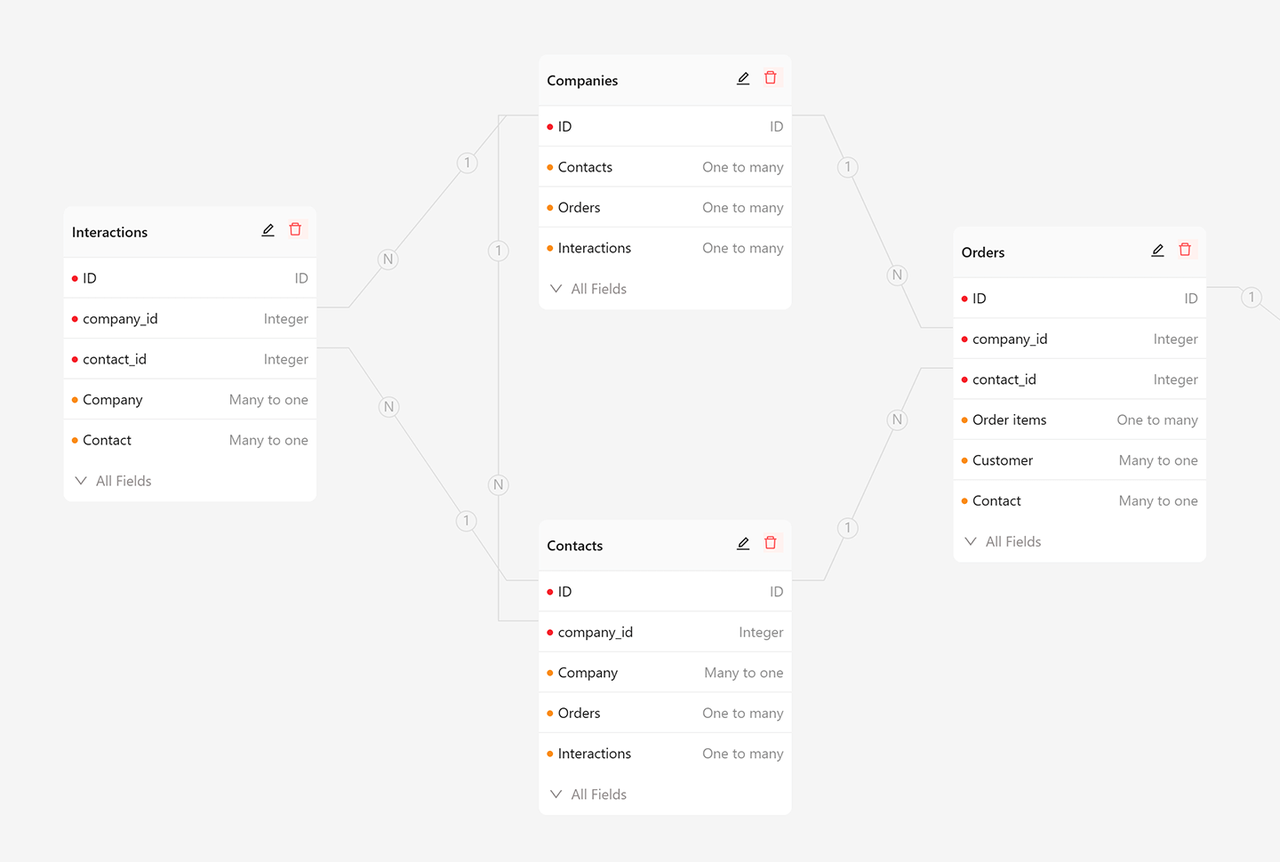
3. Plugin Architecture
Modular design allows the system to load, replace, or upgrade functions on demand, avoiding maintenance challenges caused by code coupling. The plugin mechanism should include clear lifecycle management, dependency management, and event hooks to facilitate rapid extension or customization of business functions by developers. Projects without plugin support typically have extremely high extension costs.
✅ Example: All functions in NocoBase are integrated via plugins, ensuring high extensibility.
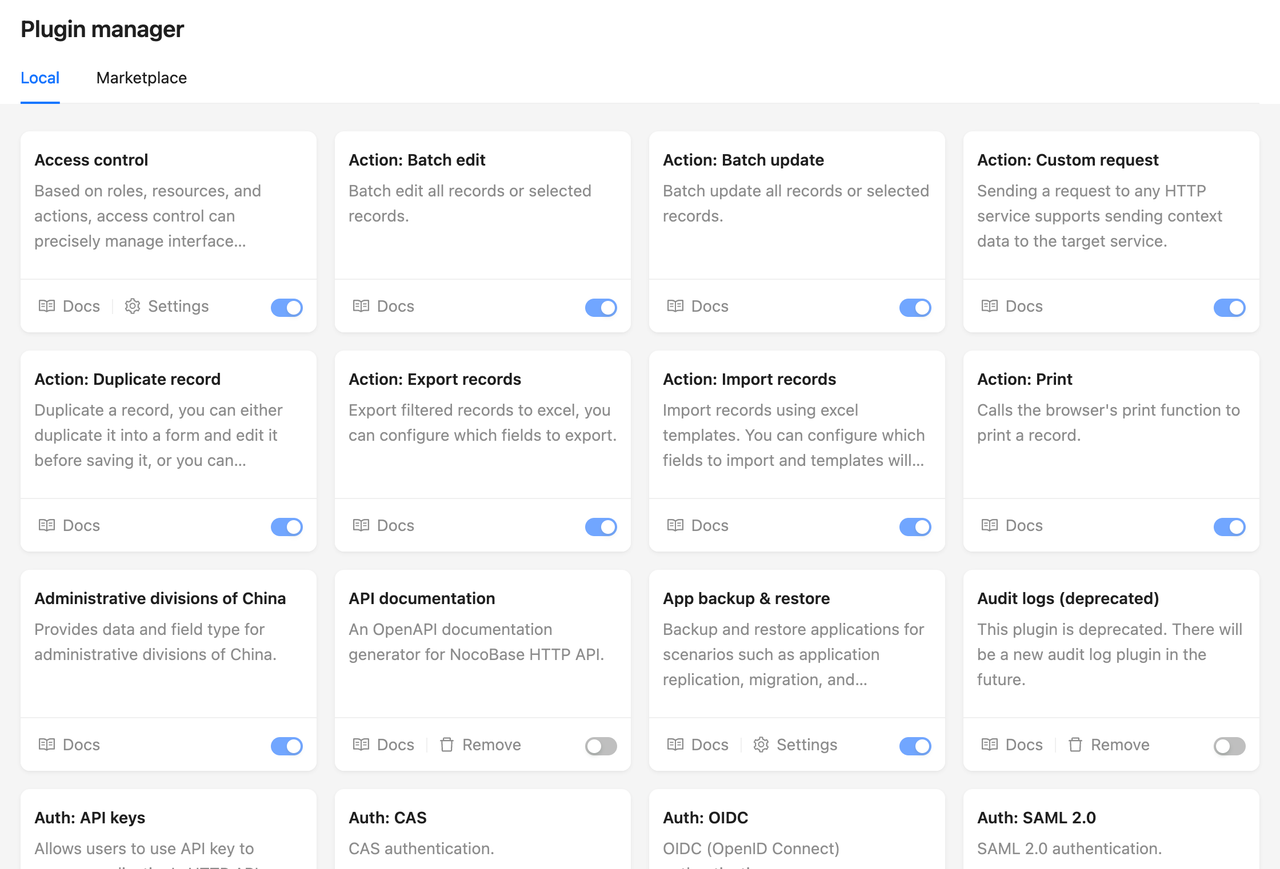
4. Automation and Workflow
Business processes are complex and changeable, making manual operations costly and error-prone. A backend system with a built-in workflow engine can complete approval processes, status transitions, message notifications, and automatic triggering of external APIs through drag-and-drop configuration or minimal coding, significantly enhancing business flexibility and automation.
✅ Example: NocoBase provides a powerful workflow plugin, allowing users to design and automate complex business processes via a visual interface.

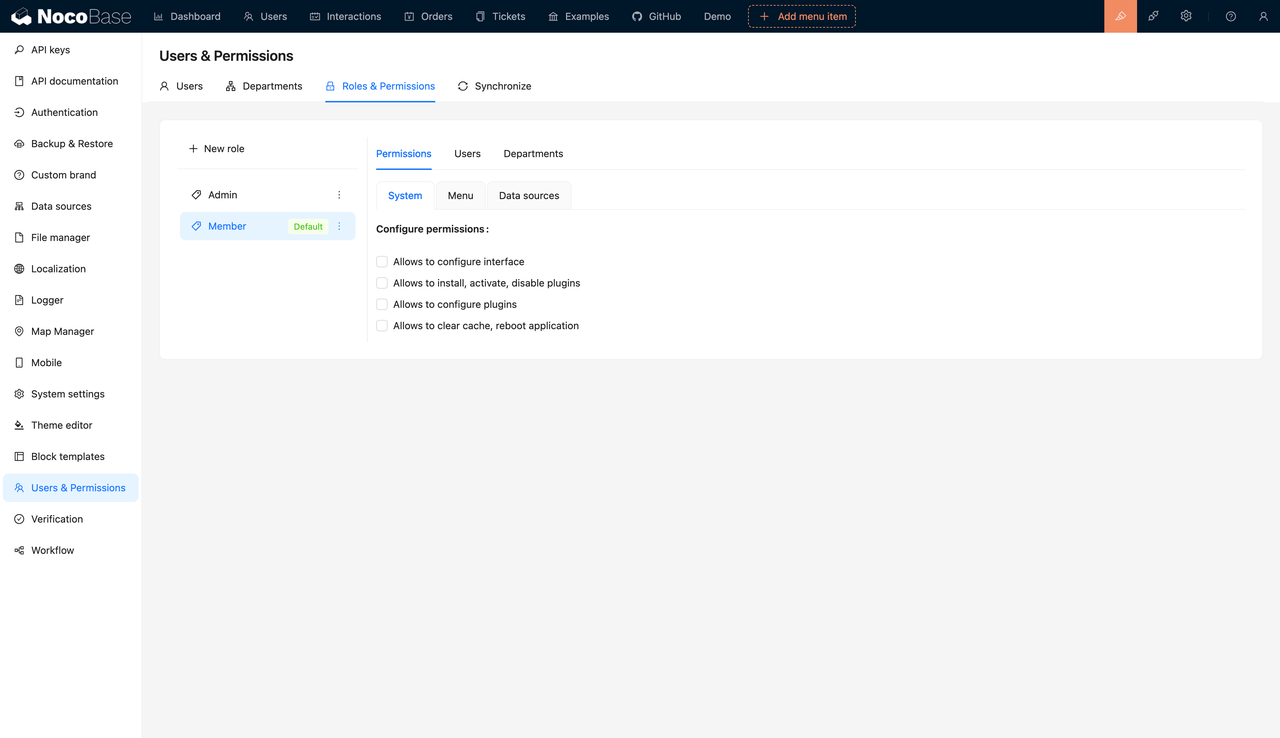
5. Permission Control Capabilities
The granularity of the permission system directly affects data security and the system’s support for multi-role scenarios. An ideal backend should support permission control based on users, roles, organizations, or even specific data. For example, restricting different departments to access different data or allowing certain users to view only partial fields are common requirements in real-world scenarios.
✅ Example: NocoBase offers highly flexible and intuitive permission control, enabling users to customize across multiple levels based on roles and conditions.
6. UI Customization Capabilities
The UI flexibility of a backend system impacts practical usage efficiency and user experience. It should support menu configuration, field display control, custom component injection, theme style modification, etc., which are particularly important for scenarios requiring integration with existing systems or front-end pages.
✅ Example: NocoBase provides an intuitive WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) UI, allowing users to quickly build and configure front-end interfaces without coding.
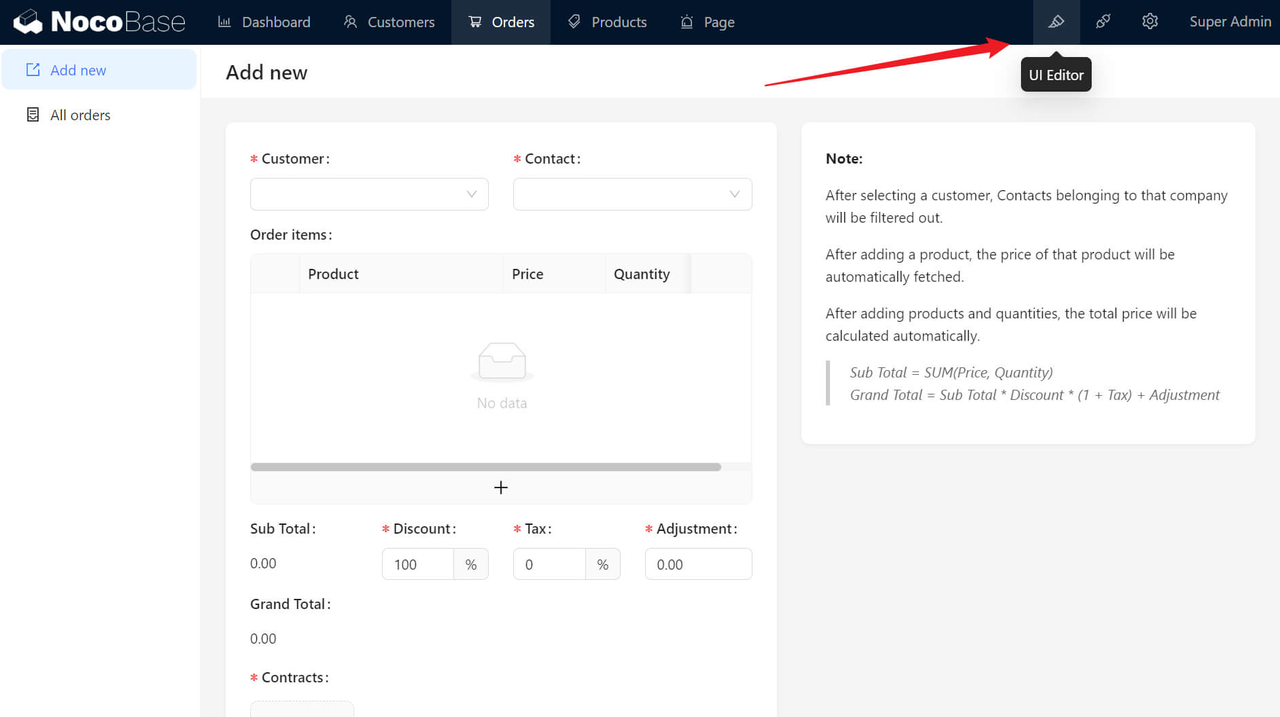
Conclusion
When selecting an open-source Admin Dashboard project, besides focusing on current functional requirements, it is crucial to prioritize the system’s extensibility and customization capabilities. The above six dimensions form a practical evaluation framework, helping technical teams avoid the trap of “unreliable late-stage transformation” and achieve continuous system evolution.
💡 Take NocoBase as an example: it is an open-source no-code platform with a complete plugin architecture and data modeling system. You can design data structures through an intuitive WYSIWYG interface, register APIs via plugins, trigger actions automatically through workflows, and implement complex data access rules in the permission system.
More importantly, both the front-end and back-end of NocoBase support extended development, enabling a transition from “simple configuration” to “deep customization”—especially suitable for technical teams that require flexibility and control.
Related reading:
- Top 11 Open-Source Admin Dashboard Projects on GitHub
- Top 6 Core App Dashboard Building Tools
- Deep Dive: Low Code/No Code Integration Capabilities
- How to Create a Good Data Model?
- ⭐️ Top 10 Open-source Workflows Projects with the Most GitHub Stars
- Complete Guide to Efficient Business Application Development